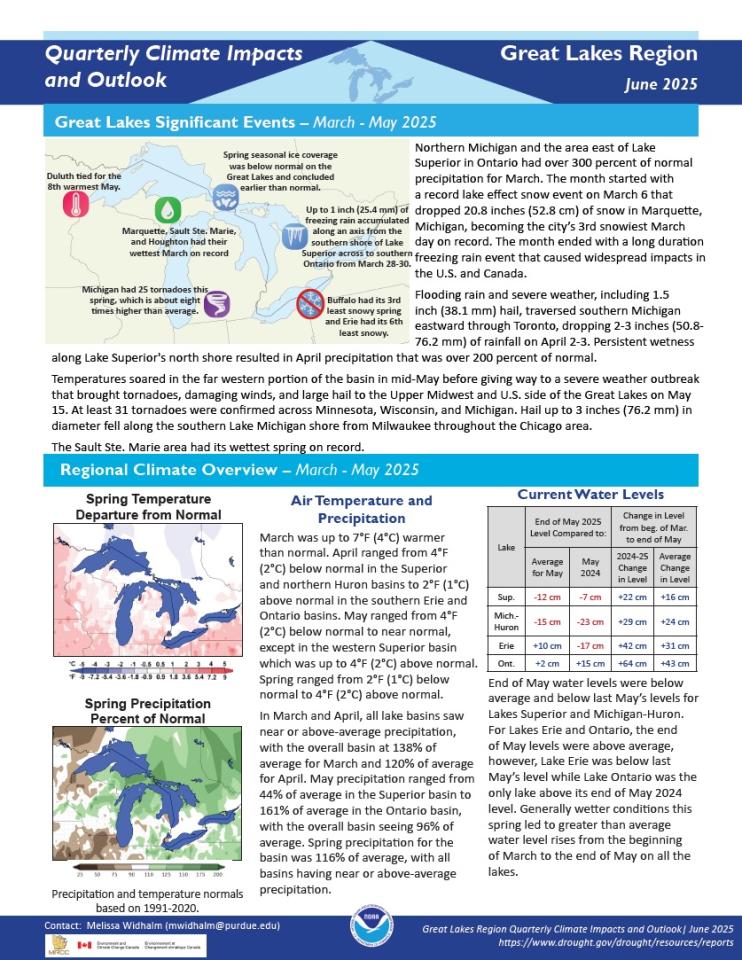
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for March–May 2025. Dated June 2025.
Spring temperatures ranged from 2°F (1°C) below normal to 4°F (2°C) above normal. Spring precipitation for the basin was 116% of average, with all basins having near or above-average precipitation.
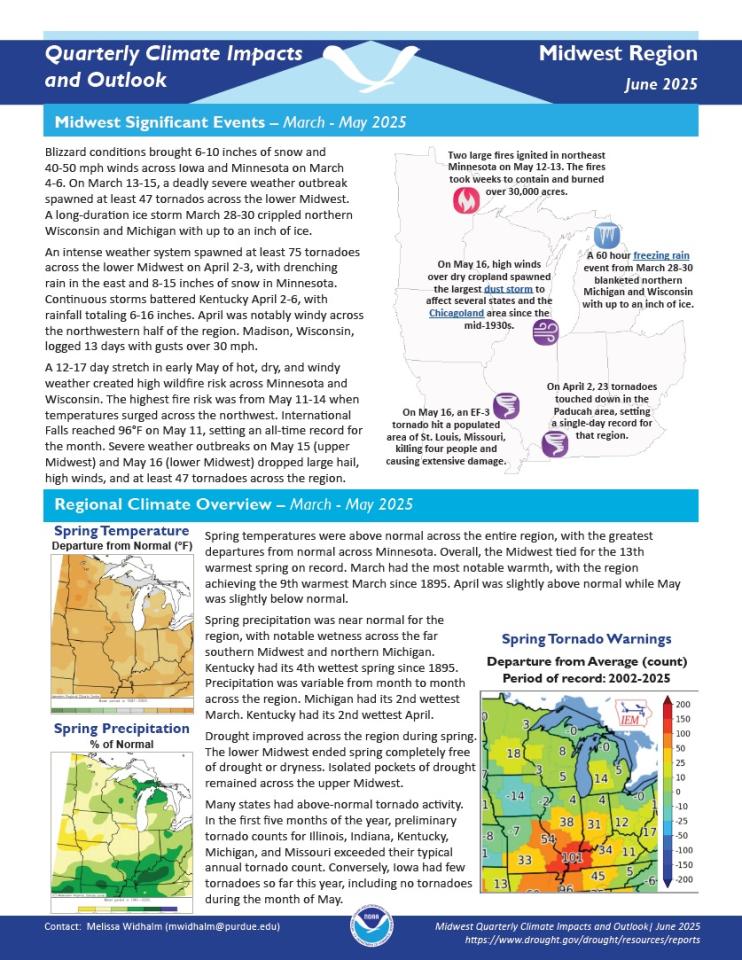
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Midwest Region for March–May 2025. Dated June 2025.
Spring temperatures were above normal across the entire region, with the greatest departures from normal across Minnesota. Overall, the Midwest tied for the 13th warmest spring on record. Spring precipitation was near normal for the region, with notable wetness across the far southern Midwest and northern Michigan. Kentucky had its 4th wettest spring since 1895.
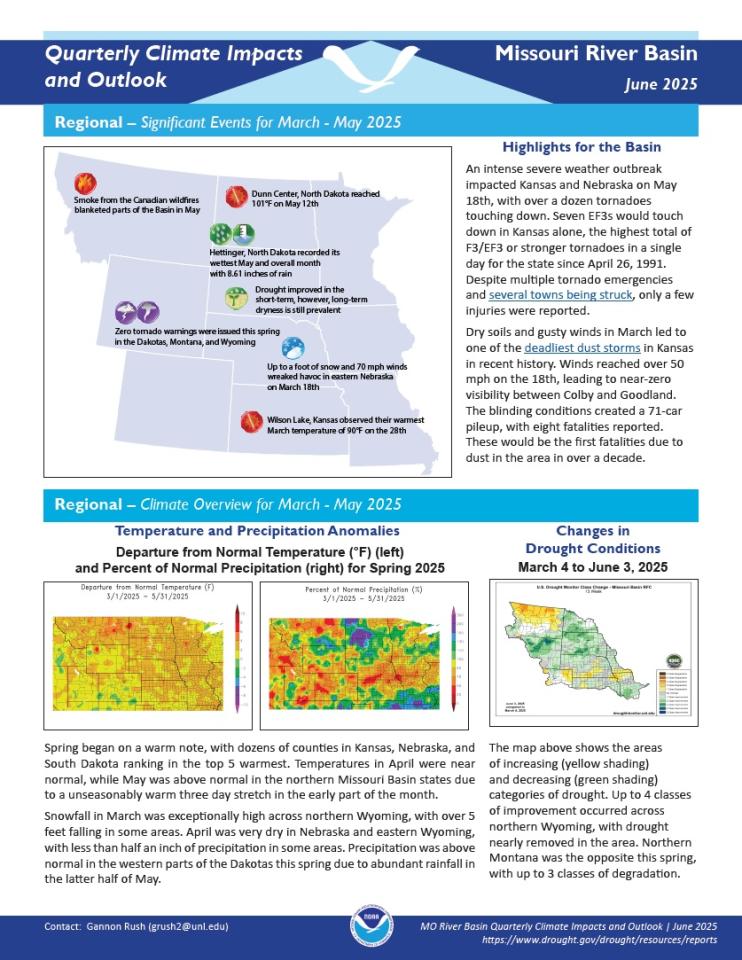
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Missouri River Basin for March–May 2025. Dated June 2025.
Spring began on a warm note, with dozens of counties in Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota ranking in the top 5 warmest. Precipitation was above normal in the western parts of the Dakotas this spring due to abundant rainfall in the latter half of May.
This report summarizes the ideas and thoughtful participation of speakers and attendees of the 2024 Midwest Drought Early Warning System (DEWS) Partners Meeting, held in Indianapolis, Indiana on August 20-22, 2024.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Missouri River Basin for December 2024–February 2025. Dated March 2025.
Despite a warm start, temperatures this winter were mostly below normal. This winter was dry, with snowfall well below normal across much of the northern and central Plains.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for December 2024–February 2025. Dated March 2025.
Winter temperatures ranged from 4°F (2°C) colder than normal to 4°F (2°C) warmer than normal. Winter precipitation was near average for all basins, with the overall basin at 99% of average.
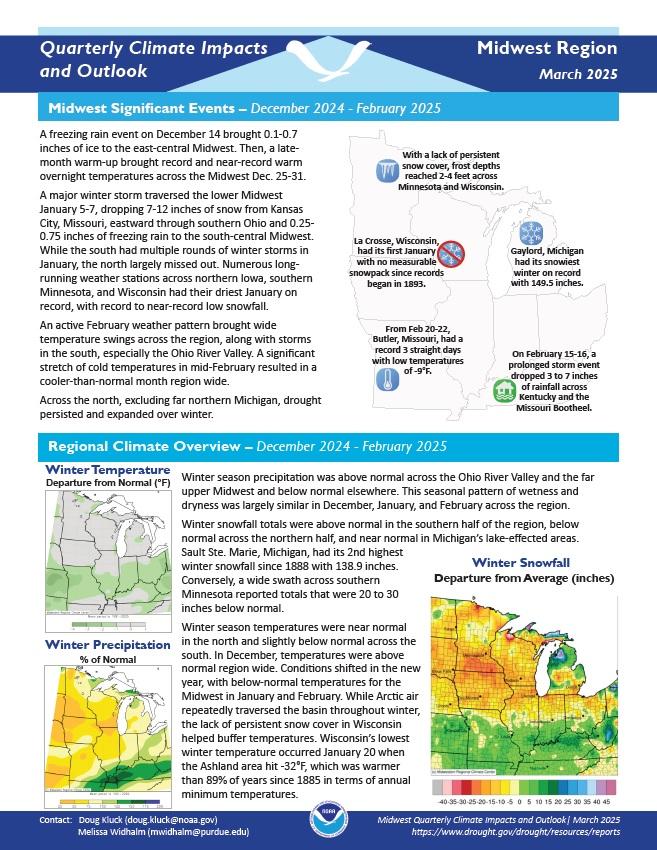
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Midwest Region for December 2024–February 2025. Dated March 2025.
Winter season temperatures were near normal in the north and slightly below normal across the south. Winter season precipitation was above normal across the Ohio River Valley and the far upper Midwest and below normal elsewhere. This seasonal pattern of wetness and dryness was largely similar in December, January, and February across the region.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for September–November 2024. Dated December 2024.
Fall temperatures were up to 7 °F (4 °C) warmer than normal. All basins were dry for fall, with the overall basin seeing 70% of average precipitation.
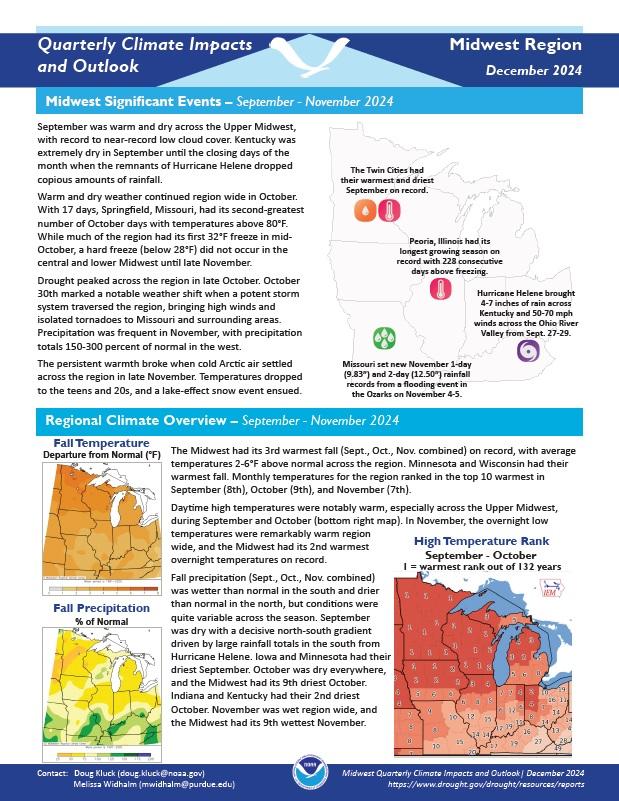
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Midwest Region for September–November 2024. Dated December 2024.
The Midwest had its 3rd warmest fall on record, with average temperatures 2-6 °F above normal across the region. Minnesota and Wisconsin had their warmest fall. Monthly temperatures for the region ranked in the top 10 warmest in September (8th), October (9th), and November (7th). Fall precipitation was wetter than normal in the south and drier than normal in the north, but conditions were quite variable across the season.
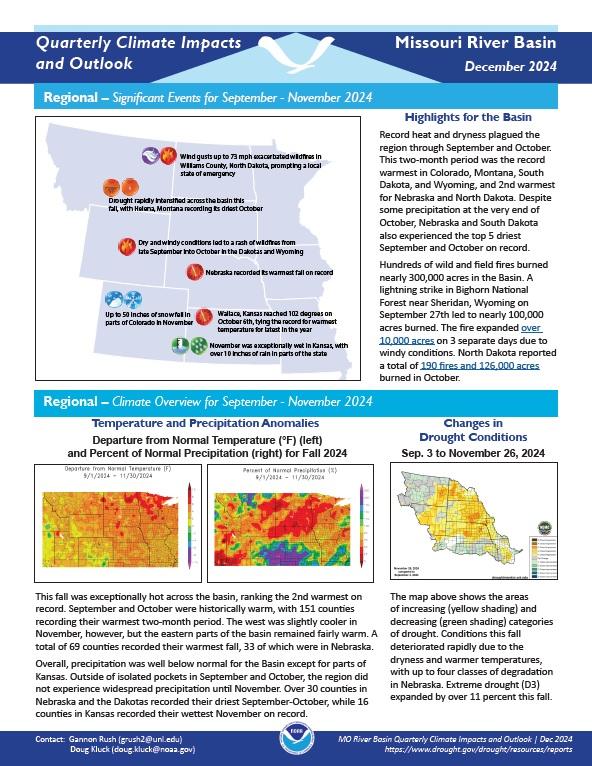
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Missouri River Basin for September–November 2024. Dated December 2024.
This fall was exceptionally hot across the basin, ranking the second warmest on record. Precipitation was well below normal for the Basin except for parts of Kansas.