Outlooks & Forecasts
1–5 Day
Sharply colder temperatures are forecast to spread over the Eastern U.S. on March 12. A second and even stronger cold front is expected to progress east from the Great Plains to the East Coast by March 16. Following this strong March cold front, below-freezing temperatures are forecast to extend as far south as Oklahoma and the Texas Panhandle. According to the National Weather Service's Weather Prediction Center, 5-day precipitation amounts from March 12-16 are forecast to exceed 1 inch, liquid equivalent, across the Great Lakes and New England. Much-needed rainfall is also anticipated for drought-stricken Florida.
Elsewhere, drier weather is forecast for the Ohio Valley, Middle to Lower Mississippi Valley, and Great Plains. During mid-March, dry weather will be accompanied by an increasing chance of record heat across California, the Great Basin, and Southwest. A powerful Kona low will bring heavy to excessive rainfall to Hawaii through at least March 14.
6–10 Day
The National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center's 6-10 day outlook (valid March 17-21) leans toward below-normal temperatures for the East, while above-normal temperatures are likely from the West Coast to the Great Plains. Above-normal temperature probabilities exceed 90% across most of California, the Great Basin, and Southwest. In contrast, Alaska is likely to be colder-than-normal.
A majority of the Lower 48 states are favored to have below-normal precipitation from March 17-21, with the largest below-normal precipitation probabilities (greater than 50% chance) forecast across the Central to Southern Great Plains, Southwest, and much of California. The wet pattern is forecast to persist for Hawaii with enhanced above-normal precipitation probabilities.
This weekly look ahead is modified from the U.S. Drought Monitor's National Drought Summary for March 10, 2026, written by Brad Pugh (NOAA's Climate Prediction Center) and Denise Gutzmer (National Drought Mitigation Center).
Official NOAA Drought Outlooks
Drought Is Predicted To...
Drought Persists
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought conditions will persist.
Drought Improves
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that existing drought conditions will improve (but not be removed).
Drought Is Removed
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will be removed.
Drought Develops
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will develop.
No Drought Present
According to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center, there is no drought, and is drought development is not predicted.
Drought Is Predicted To...
Drought Persists
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought conditions will persist.
Drought Improves
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that existing drought conditions will improve (but not be removed).
Drought Is Removed
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will be removed.
Drought Develops
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will develop.
No Drought Present
According to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center, there is no drought, and is drought development is not predicted.
The Monthly Drought Outlook predicts whether drought will develop, remain, improve, or be removed in the next calendar month.
The Seasonal Drought Outlook predicts whether drought will develop, remain, improve, or be removed in the next 3 months or so.
The Climate Prediction Center issues its Monthly Drought Outlooks on the last day of the calendar month.
The Climate Prediction Center issues its Seasonal Drought Outlooks on the third Thursday of each calendar month. Sometimes, the map is adjusted on the last day of the month to maintain consistency with the Monthly Drought Outlook.
Snow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreOfficial NOAA Precipitation Forecast
Predicted Inches of Precipitation
Less than 0.01 inch
0.01 to 0.1 inch
0.1 to 0.25 inch
0.25 to 0.5 inch
0.5 to 0.75 inch
0.75 to 1 inch
1 to 1.25 inches
1.25 to 1.5 inches
1.5 to 1.75 inches
1.75 to 2 inches
1.5 to 2 inches
2 to 2.5 inches
2.5 to 3 inches
3 to 4 inches
4 to 5 inches
5 to 7 inches
7 to 10 inches
10 to 15 inches
15 to 20 inches
More than 20 inches
Predicted Inches of Precipitation
Less than 0.01 inch
0.01 to 0.1 inch
0.1 to 0.25 inch
0.25 to 0.5 inch
0.5 to 0.75 inch
0.75 to 1 inch
1 to 1.25 inches
1.25 to 1.5 inches
1.5 to 1.75 inches
1.75 to 2 inches
1.5 to 2 inches
2 to 2.5 inches
2.5 to 3 inches
3 to 4 inches
4 to 5 inches
5 to 7 inches
7 to 10 inches
10 to 15 inches
15 to 20 inches
More than 20 inches
This map shows the amount of liquid precipitation (in inches) expected to fall over the next 1 day, according to the National Weather Service.
This map shows the amount of liquid precipitation (in inches) expected to fall over the next 7 days, according to the National Weather Service.
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast maps on Drought.gov are updated once a day and are valid from 7 a.m. Eastern that day.
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast maps on Drought.gov are updated once a day and are valid from 7 a.m. Eastern that day.
Drought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreOfficial NOAA Precipitation Outlooks
Probability of Below-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Near-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% of Near Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of near-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% of Near Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of near-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Near-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% of Near Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of near-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% of Near Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of near-normal precipitation during this period.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal precipitation 6 to 10 days in the future.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal precipitation 8 to 14 days in the future.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal (green hues) or below-normal (brown hues) precipitation over the next calendar month. White areas indicates equal chances of above- or below-normal precipitation.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal (green hues) or below-normal (brown hues) precipitation over the next three months. White areas indicates equal chances of above- or below-normal precipitation.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 6–10 day precipitation outlook daily.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 8–14 day outlooks daily.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their monthly precipitation outlook on the third Thursday of each calendar month and again on the last day of each calendar month.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their seasonal precipitation outlook on the third Thursday of each calendar month.
Drought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreOfficial NOAA Temperature Outlooks
Probability of Below-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Near-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% of Near Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of near-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% of Near Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of near-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Near-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% of Near Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of near-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% of Near Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of near-normal temperatures during this period.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal temperatures 6 to 10 days in the future.
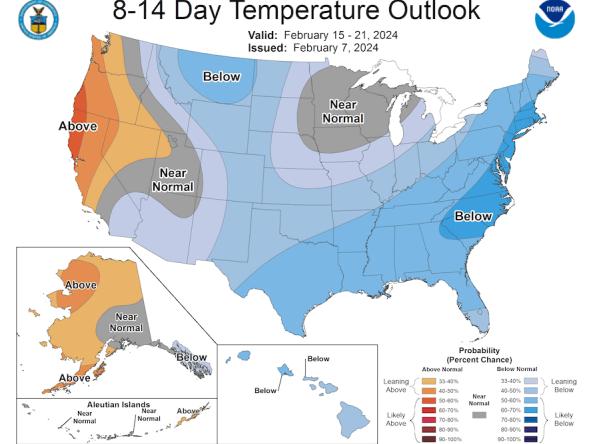
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal temperature 8 to 14 days in the future.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal (red hues) or below-normal (blue hues) temperatures over the next calendar month. White areas indicates equal chances of above- or below-normal temperatures.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal (red hues) or below-normal (blue hues) temperatures over the next three months. White areas indicates equal chances of above- or below-normal temperatures.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 6–10 day outlooks daily.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 8–14 day outlooks daily.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their monthly temperature outlook on the third Thursday of each calendar month and again on the last day of each calendar month.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their seasonal temperature outlook on the third Thursday of each calendar month.
Air temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreOfficial NOAA Fire Weather Outlook
Forecast Risk of Fire Weather
Elevated
Fire weather conditions are forecast to be elevated for temperature, wind, and relative humidity. Learn more about these designations.
Critical
Fire weather conditions are forecast to be critical for temperature, wind, and relative humidity. Learn more about these designations.
Extremely Critical
Fire weather conditions are forecast to be extremely critical for temperature, wind, and relative humidity. Learn more about these designations.
Isolated Dry Thunderstorms
The Storm Prediction Center has issued a forecast for isolated dry thunderstorms. This heightens the risk of fire ignition due to cloud-to-ground lightning, assuming a dry fuel bed. Learn more about these designations.
Scattered (Critical) Dry Thunderstorms
The Storm Prediction Center has issued a forecast for scattered (critical) dry thunderstorms. This heightens the risk of fire ignition due to cloud-to-ground lightning, assuming a dry fuel bed. Learn more about these designations.
The National Weather Service's Storm Prediction Center produces daily fire weather outlooks, which delineate areas of the continental U.S. where pre-existing fuel conditions, combined with forecast weather conditions, will result in a significant threat for the ignition and/or spread of wildfires. This map shows the 1-day fire weather outlook.
This map is updated daily with data from the National Weather Service's Storm Prediction Center. View more fire weather outlooks.
Extreme weather events can interact or cascade—where one disaster event triggers or changes the probability of another event. For example, drought conditions can increase the probability of large-scale wildfires, and droughts are often accompanied by extreme heat. By including drought in multi-hazard planning, a community can consolidate its resources and develop coordinated responses before a disaster.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreOfficial NOAA River Stage (Level) Forecast
Maximum Forecast River Stage
Major Flood
According to the National Weather Service, the Major Flood stage indicates "extensive inundation of structures and roads, significant evacuations of people, and/or transfer of property to higher elevations."
Moderate Flood
According to the National Weather Service, the Moderate Flood stage indicates "some inundation of structures and roads near stream, evacuations of people, and/or transfer of property to higher elevations."
Minor Flood
According to the National Weather Service, the Minor Flood stage indicates flooding with "minimal or no property damage, but possible some public threat (e.g., inundation of roads)."
Action Stage
When a location on the river hits the Action Stage, water levels have reached a height where "action is taken in preparation for possible significant hydrological activity," according to the National Weather Service.
No Flood
According to the National Weather Service, no flooding is indicated.
Low Water
According to the National Weather Service, the Low Water Threshold is the stage at which "low water levels begin to have significant negative impacts on a water-related industry or user community."
River forecast data from the National Weather Service's National Water Prediction Service (NWPS) provide valuable information about the chances of flood occurring. These river stage/flow forecasts show the maximum forecast flood category, taking into account past precipitation and the precipitation amounts expected approximately 48 hours into the future from the forecast issuance time.
River gauge forecasts from the National Weather Service are updated daily.
Periods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreExtreme weather events can interact or cascade—where one disaster event triggers or changes the probability of another event. For example, drought conditions can increase the probability of large-scale wildfires, and droughts are often accompanied by extreme heat. By including drought in multi-hazard planning, a community can consolidate its resources and develop coordinated responses before a disaster.
Learn MoreIn a drought, lower water levels or snowpack can affect the availability of recreational activities and associated tourism, and a resulting loss of revenue can severely impact supply chains and the economy. Drought—as well as negative perceptions of drought, fire bans, or wildfires—may also result in decreased visitations, cancellations in hotel stays, a reduction in booked holidays, or reduced merchandise sales.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
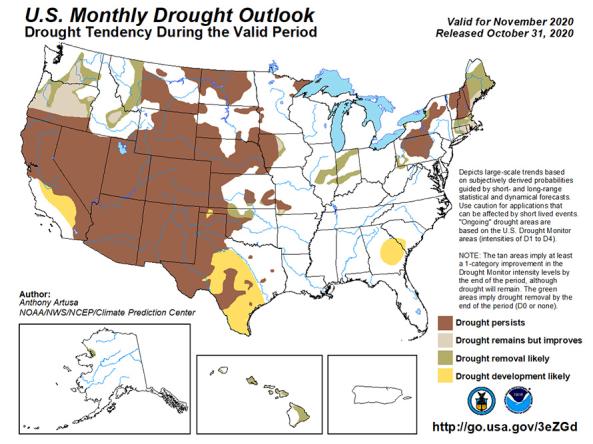
Learn MoreThe U.S. Monthly Drought Outlook predicts whether drought will emerge, stay the same or get better over the next 30 days or so.
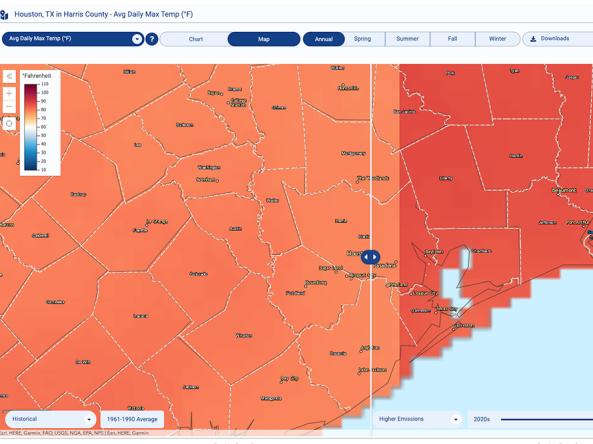
The Climate Explorer offers graphs and maps of observed and projected temperature, precipitation, and related climate variables for every county in the contiguous United States, helping people asse
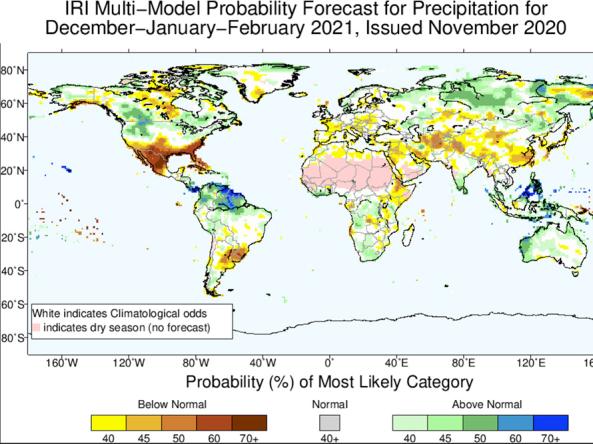
Worldwide predictions for temperature and precipitation from the International Research Institute (IRI) for Climate and Society at Columbia University.
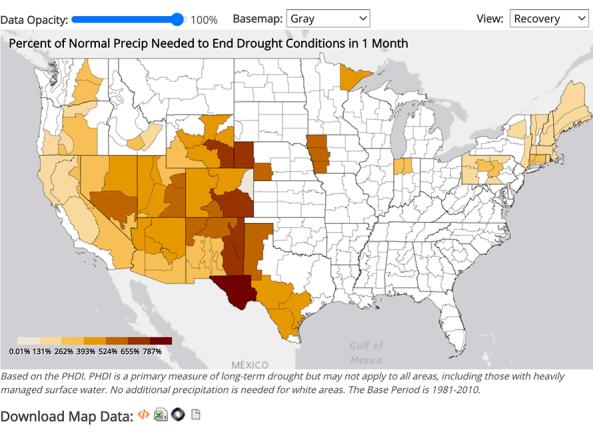
NCEI provides precipitation data that can be used to show probability or the amount of precipitation to ameliorate or end a drought at different monthly scales.
The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) produces temperature and precipitation outlooks for the U.S., including 6-10 day, 8-14 day, monthly, and seasonal outlooks.
The National Weather Service (NWS) Climate Prediction Center (CPC) produces monthly and seasonal drought outlooks based on Soil Moisture (CAS).

Challenges with Predicting Drought
Pressure Systems
High pressure systems, which hinder cloud formation and lead to low relative humidity and precipitation, can cause drought. When large-scale anomalies in atmospheric circulation patterns last for months or seasons, prolonged drought occurs (NDMC).
Temperate Zone Forecast Reliability
In temperate regions (above 30 north latitude), long-range forecasts have limited reliability. Due to differences in observed conditions and statistical models, reliable forecasts for temperate regions may not be attainable for a season or more in advance (NDMC).
Interconnected Variables
Anomalies in precipitation and temperature may last from several months to several decades, and how long they last can depend on air–sea interactions, soil moisture, land surface processes, topography, and weather systems at the global scale (NDMC).
ENSO and Global Weather Patterns
Teleconnections, such as ENSO and La Niña events, are atmospheric interactions between widely separated regions. Understanding these teleconnections can help in forecasting droughts, floods, tropical storms, and hurricanes (NDMC).