Water Supply
When drought impacts affect the water supply—the water levels in streams, reservoirs, and groundwater—it is known as hydrological drought. Periods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities.
Hydrological Drought

According to the National Drought Mitigation Center, hydrological drought results from precipitation shortfalls on the surface or subsurface water supply—affecting streamflow, reservoir and lake levels, and groundwater.
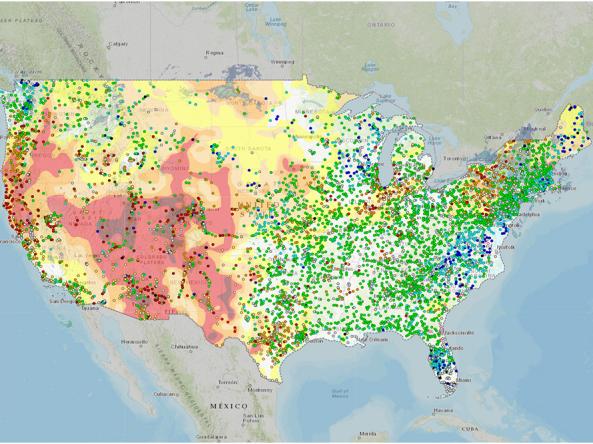
This map shows current streamflow conditions at U.S. Geological Survey streamgages, compared to historical conditions for the same day of the year. Click on a streamgage to view more information. These streamflow data are provisional and subject to revision.
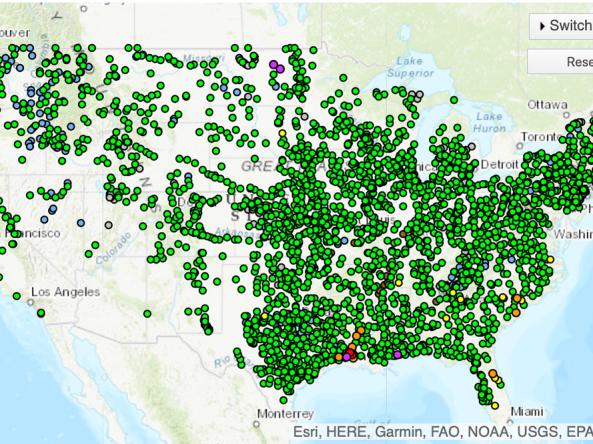
This map shows streamflow conditions averaged over the last 28 days, compared to historical conditions for the same time period. Click on a streamgage to view current data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
This map shows the amount of liquid precipitation (in inches) expected to fall over the next 7 days, according to the National Weather Service.
Periods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreStreamflow Conditions
Record Low
Estimated streamflow is the lowest value recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Below Normal (<10th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 0–10th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Below Normal (10th–25th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 10th–25th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Normal (25th–75th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 25th–75th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Above Normal (75th–90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 75th–90th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Above Normal (>90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 90th–100th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Record High
Estimated streamflow is the highest value ever measured at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Not Ranked
A flow category has not been computed for this gauge, for example due to insufficient historical data or no current streamflow estimates.
Streamflow Conditions
Record Low
Estimated streamflow is the lowest value recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Below Normal (<10th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 0–10th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Below Normal (10th–25th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 10th–25th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Normal (25th–75th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 25th–75th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Above Normal (75th–90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 75th–90th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Above Normal (>90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 90th–100th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Record High
Estimated streamflow is the highest value ever measured at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Not Ranked
A flow category has not been computed for this gauge, for example due to insufficient historical data or no current streamflow estimates.
Predicted Inches of Precipitation
Less than 0.01 inch
0.01 to 0.1 inch
0.1 to 0.25 inch
0.25 to 0.5 inch
0.5 to 0.75 inch
0.75 to 1 inch
1 to 1.25 inches
1.25 to 1.5 inches
1.5 to 1.75 inches
1.75 to 2 inches
1.5 to 2 inches
2 to 2.5 inches
2.5 to 3 inches
3 to 4 inches
4 to 5 inches
5 to 7 inches
7 to 10 inches
10 to 15 inches
15 to 20 inches
More than 20 inches
This map shows current streamflow conditions at U.S. Geological Survey streamgages, compared to historical conditions for the same day of the year. Click on a streamgage to view more information. These streamflow data are provisional and subject to revision.
This map shows streamflow conditions averaged over the last 28 days, compared to historical conditions for the same time period. Click on a streamgage to view current data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
This map shows the amount of liquid precipitation (in inches) expected to fall over the next 7 days, according to the National Weather Service.
This map updates daily on Drought.gov. View the most recent real-time streamflow data via USGS.
This map updates daily on Drought.gov. View the most recent real-time streamflow data via USGS.
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast maps on Drought.gov are updated once a day and are valid from 7 a.m. Eastern that day.
Periods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
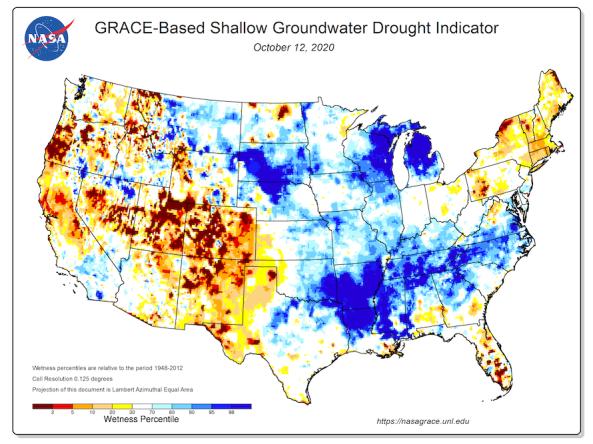
Learn MoreGroundwater and soil moisture drought indicators based on terrestrial water storage observations derived from GRACE satellite data and integrated with other observations, produced each week by NASA
The National Water Dashboard is an interactive map viewer that shows provisional real-time water data from more than 13,000 USGS observation stations in context with weather-related data
The National Weather Service's National Water Prediction Service (NWPS) provides river stage observations and forecasts and long-range river flood outlooks across the lower 48 Unite
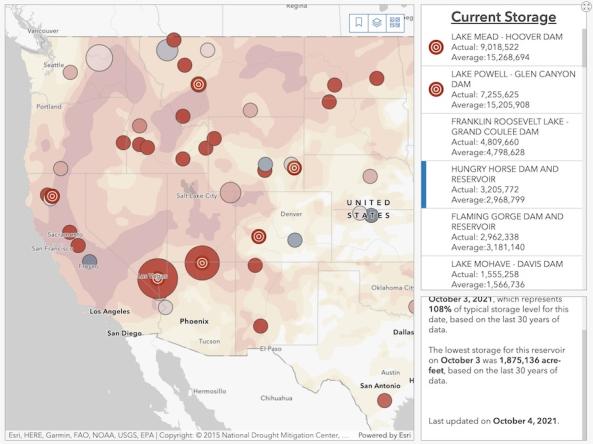
The Bureau of Reclamation's interactive Reservoir Storage Dashboard provides current conditions for 44 major Reclamation reservoirs and comparisons with historical storage data.
A resource for information about the USDA Natural Resource Conservation Service's work relating to water quality and quantity.

Impacts and Related Content
Timing
According to the National Drought Mitigation Center, the effects of hydrological drought are usually not seen until much later than those from meteorological and/or agricultural drought, as it takes longer for impacts—such as decreases in groundwater levels—to be seen in the hydrological system.
Competition/Restrictions
Groundwater and surface water from rivers and reservoirs are used in many ways—including electricity generation, recreation, wildlife habitat, flood control, and agricultural irrigation. Drought conditions can exacerbate competition for the use of the depleted resource and trigger restrictions based on prior water rights, creating conflict between water users.
Conjunctive Water Management
To manage for drought and climate extremes, water managers increasingly coordinate the use of both surface water and groundwater to utilize overall water supply more efficiently and diversify water management portfolios.
By Sector | Water Utilities
Drought impacts on water utility operations range from loss of water supply to increased costs and reduced revenues.
Drought resilience for water utilities includes the ability to respond to immediate water supply threats, as well as considering long-term conditions and planning for permanent solutions.
Forecast-Informed Reservoir Operations (FIRO)
FIRO is a proposed management strategy that uses data from watershed monitoring and modern weather and water forecasting to help water managers selectively retain or release water from reservoirs in a manner that reflects current and forecasted conditions. Western water managers require improved long-range forecasting of precipitation to more effectively manage water resources for both extreme wet and dry conditions. FIRO is being developed and tested as a collaborative effort in the Russian River Basin (Lake Mendocino), the Santa Ana River Basin (Prado Dam), and the Yuba-Feather River Basins.