Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for March–May 2024. Dated June 2024.
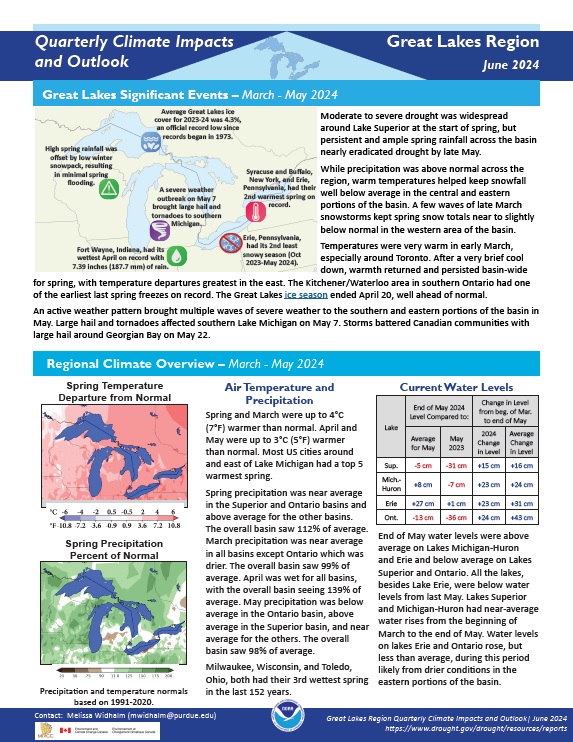
Spring and March were up to 4°C (7°F) warmer than normal. April and May were up to 3°C (5°F) warmer than normal. Most U.S. cities around and east of Lake Michigan had a top 5 warmest spring. Spring precipitation was near average in the Superior and Ontario basins and above average for the other basins. The overall basin saw 112% of average precipitation.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024.
Winter was 2°C (4°F) to more than 6°C (11°F) above normal. The basin saw 78% of average precipitation for winter, with all basins but Ontario being dry.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for September–November 2023. Dated December 2023.
Fall temperatures in the region were up to 2°C (4°F) above normal. The overall basin saw 69% of average precipitation with all lake basins being dry.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for June–August 2023. Dated September 2023.
Summer temperatures were 2°C (4°F) below normal in the Erie basin, to near normal elsewhere. Summer precipitation was 96% of average, with Superior dry, Ontario wet, and the others near average.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for March–May 2023. Dated June 2023.
Spring temperatures ranged from 2°C (4°F) below normal to 1°C (2°F) above normal. Spring precipitation was 90% of average, with the Erie basin being dry, Superior basin being wet, and the other basins near average.
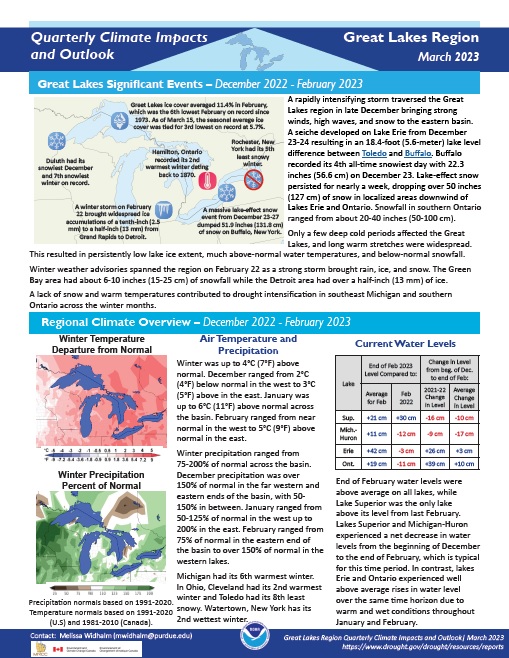
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for December 2022–February 2023. Dated March 2023.
Winter was up to 4°C (7°F) above normal. Winter precipitation ranged from 75%–200% of normal across the basin.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these climate outlooks to inform the public about recent climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for September–November 2022. Dated December 2022.
Fall and September were up to 2°C (4°F) warmer than normal. Fall precipitation was 78% of average, and all basins were dry.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these climate outlooks to inform the public about recent climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for June–August 2022. Dated September 2022.
June, July, and summer were within 1°C (2°F) of normal for most of the basins, with a few U.S. locations that were warmer. The overall basin saw 90% of average precipitation for summer, and all basins were drier than normal.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for March–May 2022. Dated June 2022.
Spring ranged from 2°C (4°F) below normal in the Superior basin to 2°C (4°F) above normal in the Erie and Ontario basins. The overall basin saw 111% of average precipitation for spring, with Erie and Ontario being drier and the other basins being wetter.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for December 2021 - February 2022. Dated March 2022.
Winter temperatures ranged from 4°C (11°F) colder-than-normal to 1°C (2°F) warmer-than-normal. Overall, winter precipitation was 82% of average for the basin.