Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Gulf of Maine Region for September – November 2018. Dated December 2018.
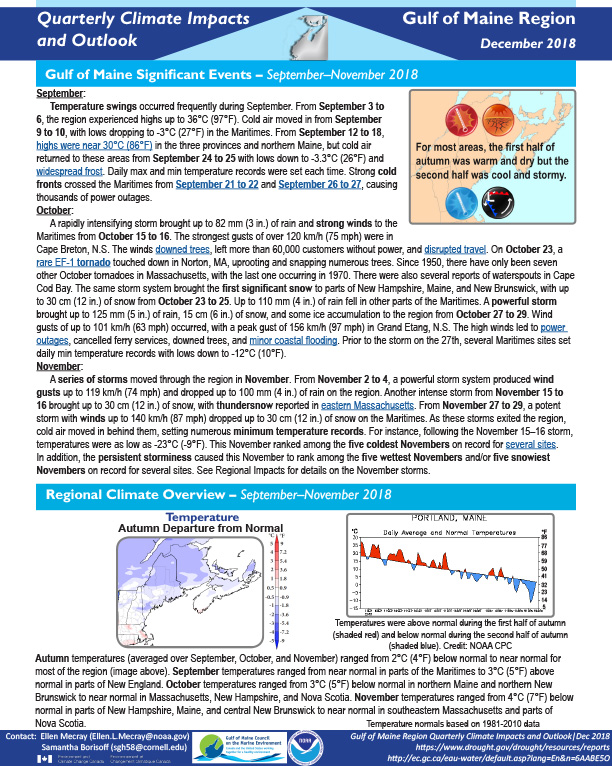
Autumn temperatures ranged from 2°C (4°F) below normal to near normal for most of the region. Autumn precipitation generally ranged from 75% of normal in northern New Brunswick to 200% of normal in southeastern Massachusetts.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Southeast Region for September – November 2018. Dated December 2018.
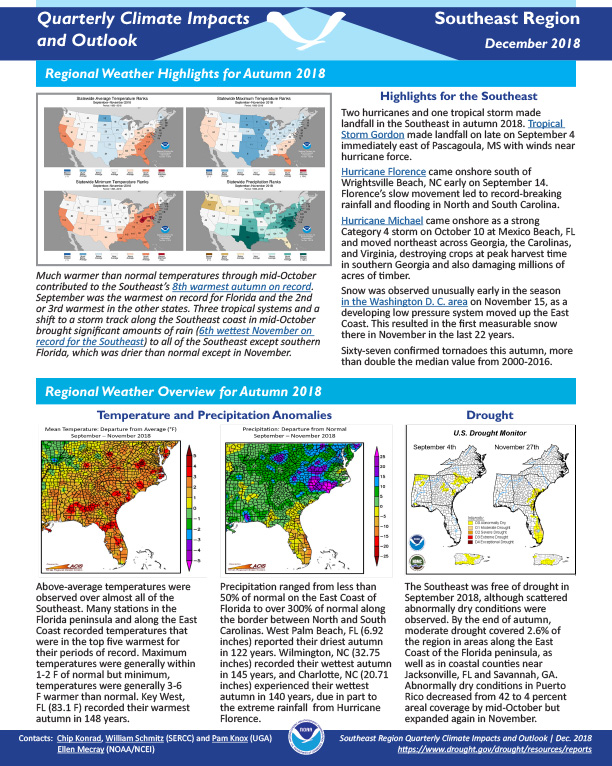
Above-average temperatures were observed over almost all of the Southeast. Precipitation ranged from less than 50% of normal on the East Coast of Florida to over 300% of normal along the border between North and South Carolinas.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for September – November 2018. Dated December 2018.
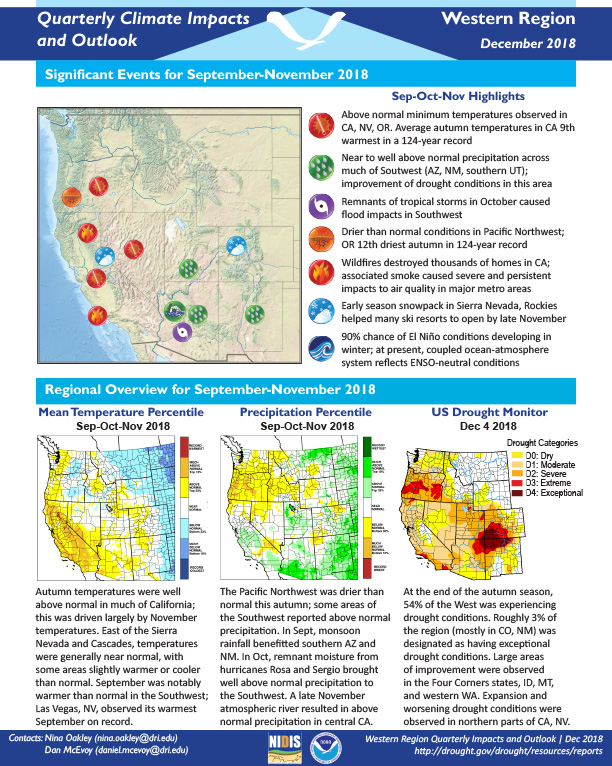
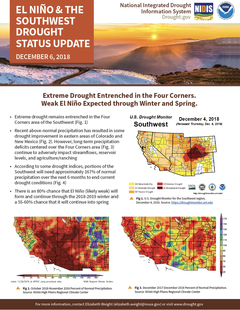
Above normal minimum temperatures were observed in California, Nevada, and Oregon. Near to well above normal precipitation was observed across much of the Southwest (Arizona, New Mexico, and southern UT) with an improvement of drought conditions in this area.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Northeast Region for September – November 2018. Dated December 2018.
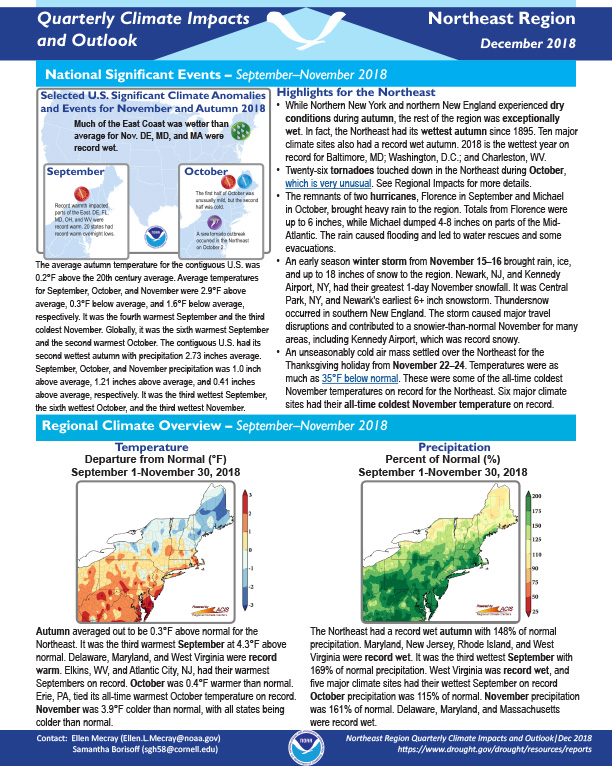
Autumn averaged out to be 0.3°F above normal for the Northeast. The Northeast had a record wet autumn with 148% of normal precipitation.
The purpose of this Northwest Florida Water Management District Water Supply Assessment update is to determine, “Whether existing and reasonably anticipated sources of water and conservation efforts are adequate to supply water for all existing legal uses and reasonably anticipated future needs and to sustain the water resources and related natural systems.” Learn more and view past water supply assessment updates on the Northwest Florida Water Management District website.
The purpose of the Alabama Drought Management Plan is to provide information and procedural details associated with Alabama’s drought planning and response activities. The 2018 revision of the Plan is now fully in accordance with the Alabama Drought Planning and Response Act and the subsequent regulations promulgated in support of that Act.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for Hawaii and the U.S. Pacific Islands Region for August – October 2018. Dated November 2018.
Includes significant events, regional climate overview, and sectoral impacts for August – October 2018; regional outlook for November 2018 – January 2019.
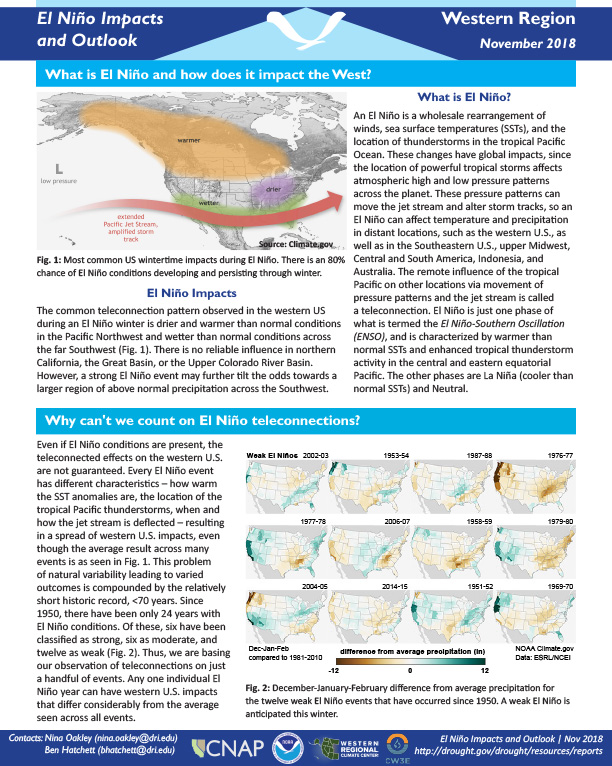
Provides a definition of El Nino; potential winter impacts; the outlook for winter temperatures and precipitation; and a look back at previous El Nino winters.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these Outlooks to inform the public about climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal at https://www.drought.gov/drought/resources/reports.
The 2019 Water Year was off to a dry start in California-Nevada. According to the U.S. Drought Monitor, ~74% of California-Nevada is in moderate (D1) to extreme drought (D3) as of December 4, 2018. Extreme drought (D3) conditions began impacting Ventura-Santa Barbara counties while D1-D2 conditions expanded over the Sierras and northern coastal California. Precipitation at the end of November into early December improved some of these conditions.