For the latest forecasts and critical weather information, visit weather.gov.
In order to ensure the inclusion of indigenous perspectives in the implementation of our DEWS, NIDIS launched a Tribal Drought Engagement initiative in January 2019 in collaboration with the Masters of the Environment Program at University of Colorado-Boulder. The project aimed to strengthen relationships with tribal resource managers across the Missouri River Basin and Midwest DEWS regions in order to effectively deliver timely and relevant drought information.
Provides information on the typical La Niña winter pattern; the La Niña outlook; potential impacts; and comparisons of conditions during previous La Niña years.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these outlooks to inform the public about climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.
Provides information on the typical La Niña winter pattern; the La Niña outlook; potential winter and spring impacts; and comparisons of conditions during previous La Niña years.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these Outlooks to inform the public about climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.
This drought early warning update was originally sent via email to the Missouri River Basin and Midwest DEWS email lists.
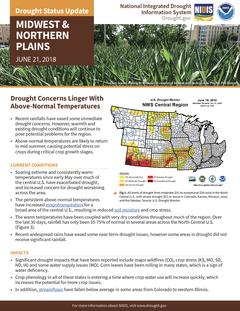
A two-page status update on drought conditions, including current conditions, impacts, and outlook, in the Midwest and Northern Plains regions for June 21, 2018.
Significant Drought Impacts Reported in Kansas, Missouri, Southeast Iowa
Extreme to Exceptional Drought Worsens in Missouri, Kansas, and Iowa Since Mid-July
- Drought conditions have increased in severity and coverage across the central United States since mid-July, particularly in MO, KS, IA, MI, MN, ND, and SD.
- Despite some recent rains, exceptional drought(D4) persists in KS and MO.
- Agriculture and water supply have been the most negatively affected by this summer’s drought conditions. Some of the recent rainfall may help soybeans and pasture recovery, but it likely fell too late to help stressed corn.
Rainfall Brings Much-Needed Drought Relief to Missouri, Kansas, and Iowa
- Recent rainfall has brought much-needed relief to the hardest-hit drought areas in MO, KS, and IA, however, at the same time, drought conditions worsened in ND.
- Although rainfall has improved conditions, drought recovery may be slow in areas that experienced extreme or exceptional drought this summer - particularly where surface water and groundwater was limited.
- Winter is typically the driest season, making autumn a key season for recovery from hydrologic drought.
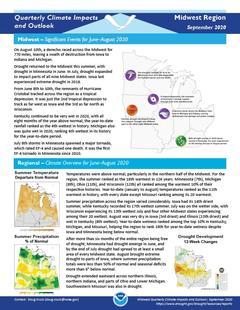
uarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Midwest Region for June – August 2020. Dated September 2020.
Temperatures were above normal, particularly in the northern half of the Midwest. For the region, the summer ranked as the 18th warmest in 126 years. Summer precipitation across the region varied considerably. Iowa had its 14th driest summer, while Kentucky recorded its 17th wettest summer.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for June – August 2020. Dated September 2020.
Summer was overall very warm across the basin. Several areas of the basin, stretching from Minnesota to Michigan and New York, had one of their top 10 warmest summers for minimum air temperature. In eastern and southern Ontario, temperatures remained above normal almost continuously from mid-June to mid-August. Summer precipitation was near or above average except in the Erie basin, with the overall basin seeing 105% of average.