For the latest forecasts and critical weather information, visit weather.gov.
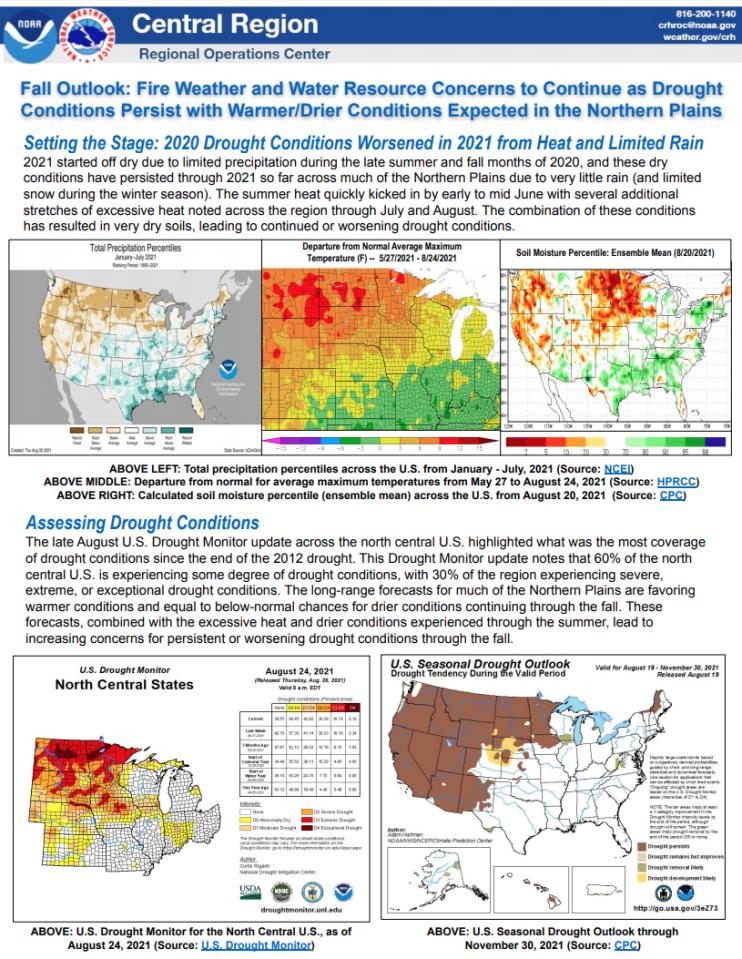
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021 Fall Hazard Outlooks in coordination with NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information and National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS); U.S. Department of Agriculture; High Plains Regional Climate Center; and National Interagency Fire Center's Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Fall hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Northern Plains.
Droughts are often thought of as slow-moving natural hazards. However, some serious droughts occur with such rapid onset that it seems as if they appear in a “flash,” rendering them and their consequences hard to predict and prepare for. These flash droughts can have substantial agricultural and economic consequences, including billions of dollars in losses.
For Fiscal Year (FY) 2022, the National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) is hosting a research competition, Coping with Drought: Building Tribal Drought Resilience. Applications should be developed by or in full partnership with tribal nations to fund the implementation of actions—together with research on those actions—to build drought resilience contained in existing plans and strategies. Plans may include, but are not limited to drought contingency plans; drought, water, or natural resource plans; agricultural resource management plans; or climate adaptation plans.
For Fiscal Year (FY) 2022, the National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) is hosting a research competition, Coping with Drought: Building Tribal Drought Resilience. Applications should be developed by or in full partnership with tribal nations to fund the implementation of actions—together with research on those actions—to build drought resilience contained in existing plans and strategies. Plans may include, but are not limited to drought contingency plans; drought, water, or natural resource plans; agricultural resource management plans; or climate adaptation plans.
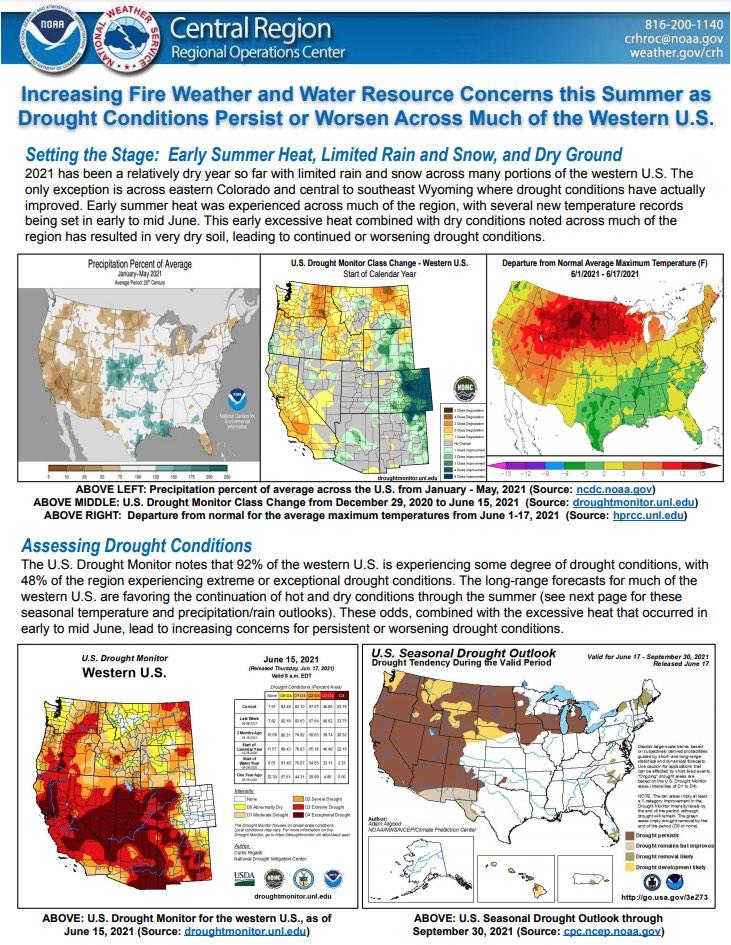
As of July 13, 2021, 89% of the West is in drought and 25% is in Exceptional (D4) Drought. Both are U.S. Drought Monitor records. Much of the West was drought free just over 14 months ago, but drought conditions began developing around May 2020. A poor summer 2020 monsoon season followed by snow drought in winter 2020-21 worsened conditions in California and the Southwest. Record-shattering temperatures and dry conditions in the Northwest in early summer 2021 caused conditions to rapidly deteriorate in a region that was already facing multi-year precipitation deficits.
On July 14, 2021, the National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) hosted an informational webinar on the Climate Program Office FY22 Coping with Drought competition on Ecological Drought.
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021 Summer Hazard Outlooks in coordination with the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS), and National Water Center; U.S. Department of Agriculture; National Weather Service River Forecast Centers; and National Interagency Fire Centers' Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Summer hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Western U.S.
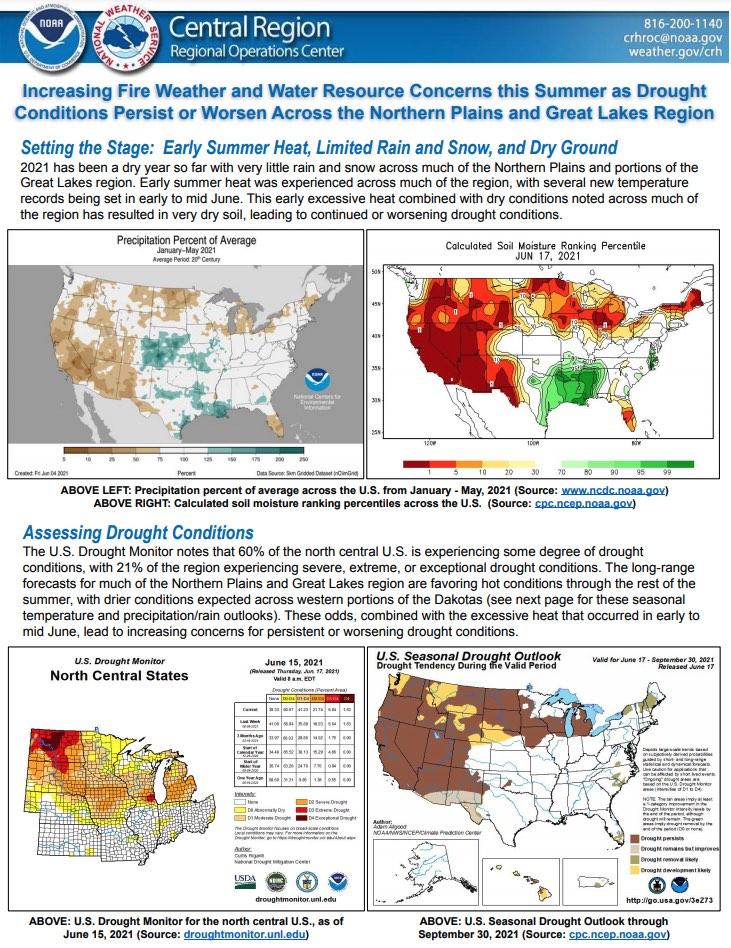
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021 Summer Hazard Outlooks in coordination with the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS), and National Water Center; U.S. Department of Agriculture; National Weather Service River Forecast Centers; and National Interagency Fire Centers' Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Summer hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Northern Plains and Great Lakes region.