Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Mid-Atlantic Region for March–May 2023. Dated June 2023.
Average temperatures for this spring were 0–2 degrees F above normal for the majority of the region. This is cooler than what was observed for the winter season, but similar to what was observed from spring 2021 to fall 2022. The majority of the region experienced drier than normal conditions (50%–75% of normal precipitation).
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Gulf of Maine Region for March–May 2023. Dated June 2023.
Spring was up to 3°C (5°F) warmer than normal. Spring precipitation ranged from 25% of normal to 125% of normal.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these climate outlooks to inform the public about recent climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.
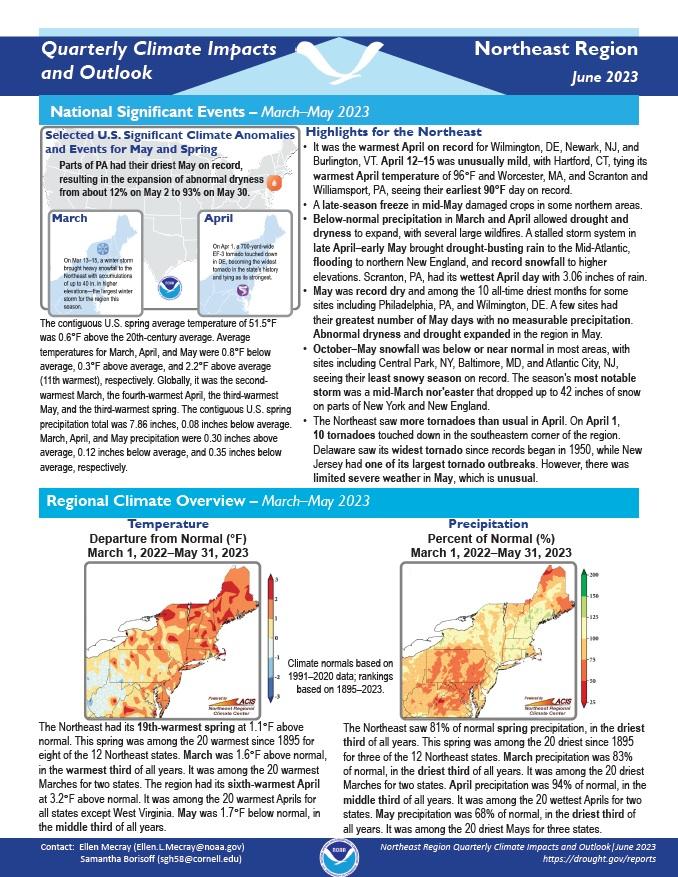
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Northeast Region for March–May 2023. Dated June 2023.
The Northeast had its 19th-warmest spring at 1.1°F above normal. This spring was among the 20 warmest since 1895 for 8 of the 12 Northeast states. The Northeast saw 81% of normal spring precipitation, in the driest third of all years. This spring was among the 20 driest since 1895 for 3 of the 12 Northeast states.
Drought is one of the costliest and deadliest climate-related disasters in the United States, necessitating public health engagement at a national level. Although drought is not typically thought of as a health hazard, the pathways to human health outcomes are prevalent and numerous. To better understand these pathways, and actions that could be taken to reduce health impacts associated with drought, NOAA’s National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) supported the first comprehensive assessment of drought and health.