Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for June - August 2021. Dated September 2021.
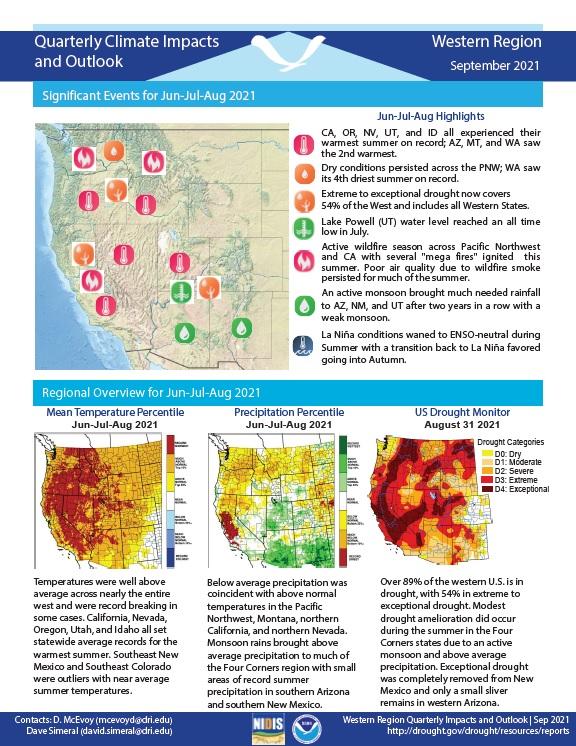
Temperatures were well above average across nearly the entire west and were record breaking in some cases. Over 89% of the western U.S. is in drought, with 54% in extreme to exceptional drought.
Severe, extreme, or exceptional drought conditions have become increasingly common throughout the western United States over the past 20 years. Abnormally dry conditions can lead to a wide range of negative economic impacts across a wide range of sectors that either directly or indirectly depend on weather-dependent ecosystem services.
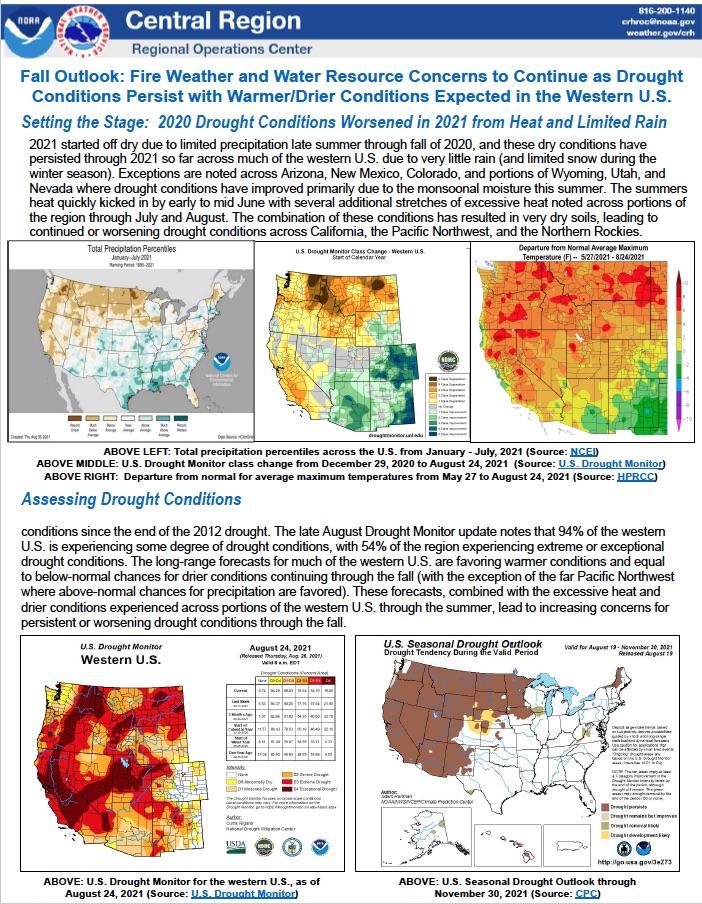
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021 Fall Hazard Outlooks in coordination with NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information and National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS); U.S. Department of Agriculture; High Plains Regional Climate Center; and National Interagency Fire Center's Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Fall hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Western U.S.
Since 2000, the Colorado River basin has been experiencing a historic, extended drought that has impacted regional water supply and other resources, such as hydropower, recreation, and ecological goods and services. During this time, the Basin has experienced its lowest 16-year period of inflow in over 100 years of record keeping, and reservoir storage in the Colorado River system has declined from nearly full to about half of capacity.
As of July 13, 2021, 89% of the West is in drought and 25% is in Exceptional (D4) Drought. Both are U.S. Drought Monitor records. Much of the West was drought free just over 14 months ago, but drought conditions began developing around May 2020. A poor summer 2020 monsoon season followed by snow drought in winter 2020-21 worsened conditions in California and the Southwest. Record-shattering temperatures and dry conditions in the Northwest in early summer 2021 caused conditions to rapidly deteriorate in a region that was already facing multi-year precipitation deficits.
As of June 22, 2021, 90% of the Southwest and California is in drought, with 40% of this region in Exceptional Drought (D4), the highest level. Twelve months prior, most of the West was drought-free, but drought conditions began developing around May 2020. High temperatures and very low rainfall totals through spring and summer of 2020 set new records across the Southwest, and the combination of extremely low soil moisture leading into winter and snow drought through winter means that run-off in the spring of 2021 has been very low.
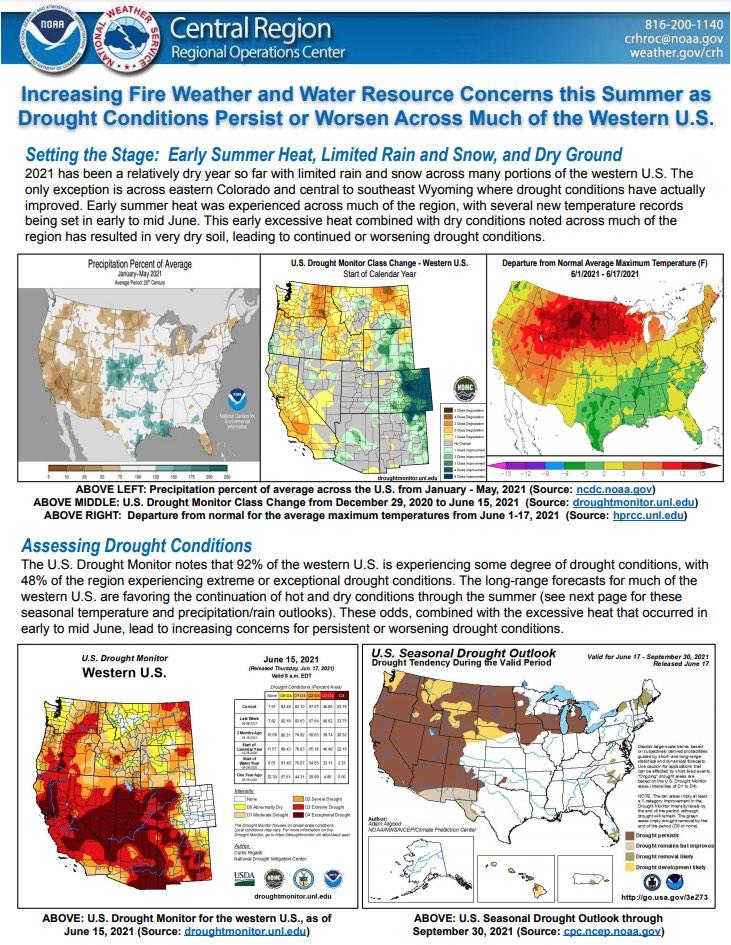
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021 Summer Hazard Outlooks in coordination with the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS), and National Water Center; U.S. Department of Agriculture; National Weather Service River Forecast Centers; and National Interagency Fire Centers' Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Summer hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Western U.S.