Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for September–November 2024. Dated December 2024.
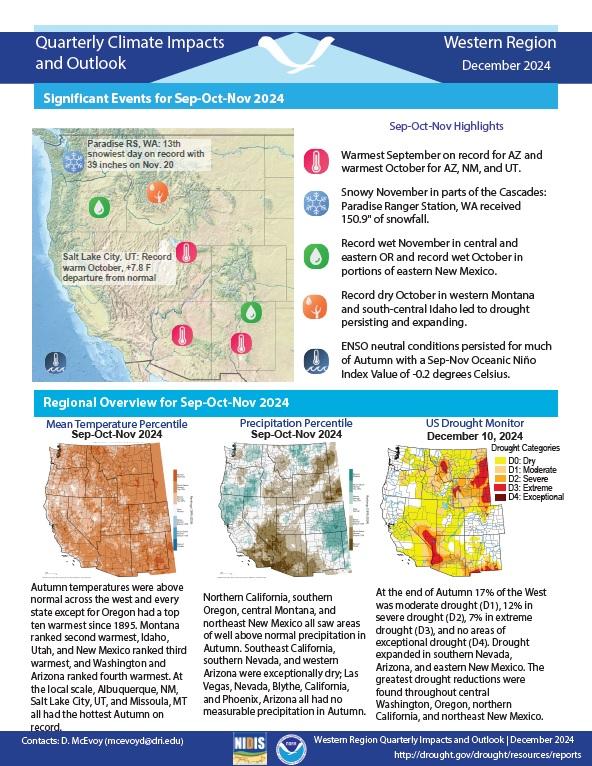
Autumn temperatures were above normal across the West, and every state except for Oregon had a top ten warmest autumn since 1895. Northern California, southern Oregon, central Montana, and northeast New Mexico all saw areas of well-above-normal precipitation in autumn. Southeast California, southern Nevada, and western Arizona were exceptionally dry.
Regional groundwater measurements in the Ogallala Aquifer show ongoing declines in aquifer water quality and quantity that are being exacerbated by warming trends and highly variable precipitation. The importance of this system, which is used for agriculture and is a main driver impacting socioeconomic activity and ecosystems in the region, cannot be overstated. Addressing regional aquifer depletion and other water-related challenges, including drought, is vital and necessary work.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for June–August 2024. Dated September 2024.
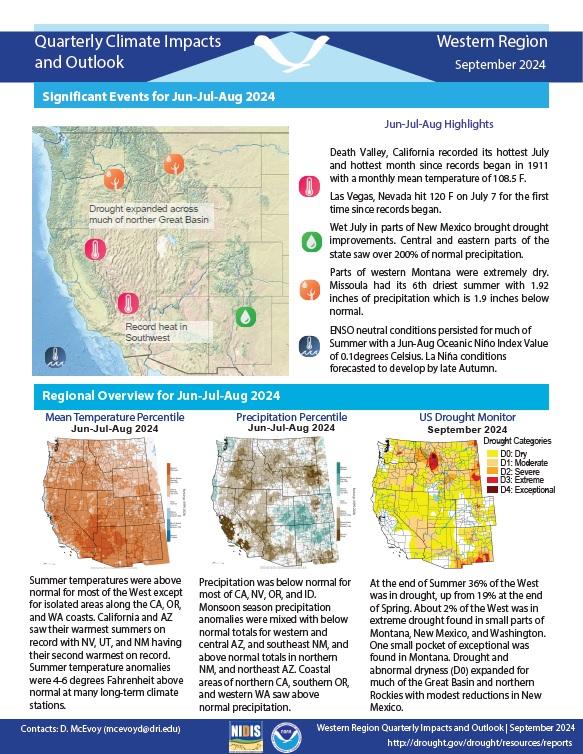
Summer temperatures were above normal for most of the West except for isolated areas along the California, Oregon, and Washington coasts. California and Arizona saw their warmest summers on record with Nevada, Utah, and New Mexico having their second warmest on record. Precipitation was below normal for most of California, Nevada, Oregon, and Idaho.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for March–May 2024. Dated June 2024.
Spring temperatures were generally near normal or below normal for most of the West. Precipitation was near-to-above normal for most of the West with north-central Arizona and southeast Montana much above normal.
From worsening water quality to respiratory and metal health impacts, drought can have profound and widespread impacts on the health of communities across the nation. To better prepare health professionals’ response to the health effects of drought, a research team from the University of Nebraska Medical Center’s College of Public Health recently released a new guide to assist healthcare providers and public health officials communicate about the health risks of drought with their patients and broader communities.