For the latest forecasts and critical weather information, visit weather.gov.
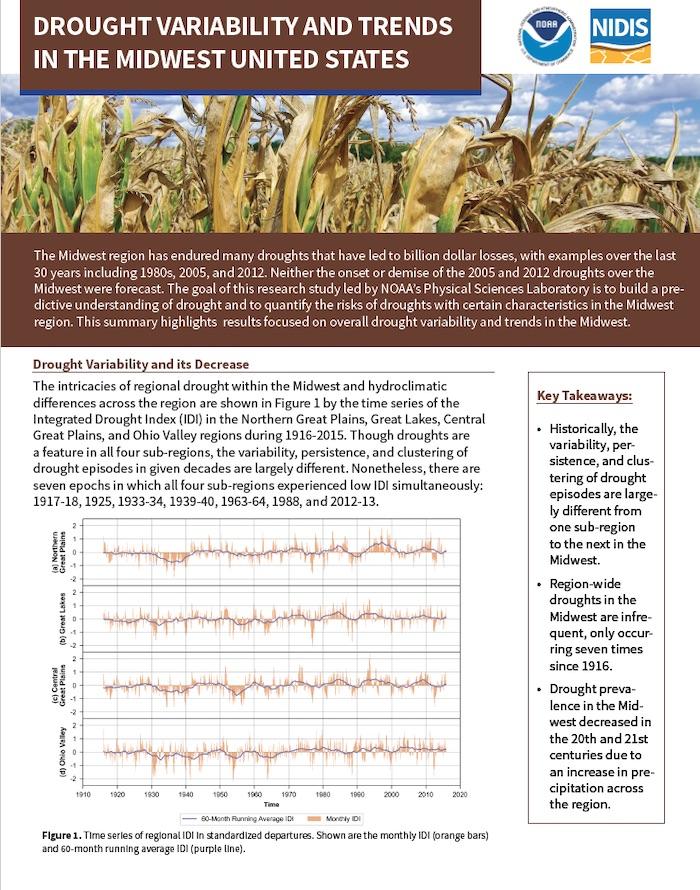
The Midwest region has endured many droughts that have led to billion dollar losses, with examples over the last 30 years including 1980s, 2005, and 2012. Neither the onset or demise of the 2005 and 2012 droughts over the Midwest were forecast. The goal of this NIDIS-funded research study led by NOAA’s Physical Sciences Laboratory is to build a predictive understanding of drought and to quantify the risks of droughts with certain characteristics in the Midwest region.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Great Lakes Region for September - November 2021. Dated December 2021.
Above-normal temperatures dominated the region throughout the fall. Precipitation was variable, with less moisture overall in the west than the east. Dryness in the western basin this fall continued a dry trend that has persisted in this area for over two years.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Midwest Region for September - November 2021. Dated December 2021.
Above-normal temperatures prevailed across the Midwest during the fall. Average temperatures were 2.6°F above-normal, ranking the 6th warmest dating back to 1895. Although fall precipitation averaged near-normal for the Midwest as a whole, it was highly variable by region and by month.
Since 2011, the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s Central Regional Climate Services Director, American Association of State Climatologists, U.S. Department of Agriculture Climate Hubs and Office of the Chief Economist, National Drought Mitigation Center (NDMC), and National Integrated Drought Information System have partnered to provide monthly climate and drought updates to stakeholders who live, work, or have interests in the North Central U.S.
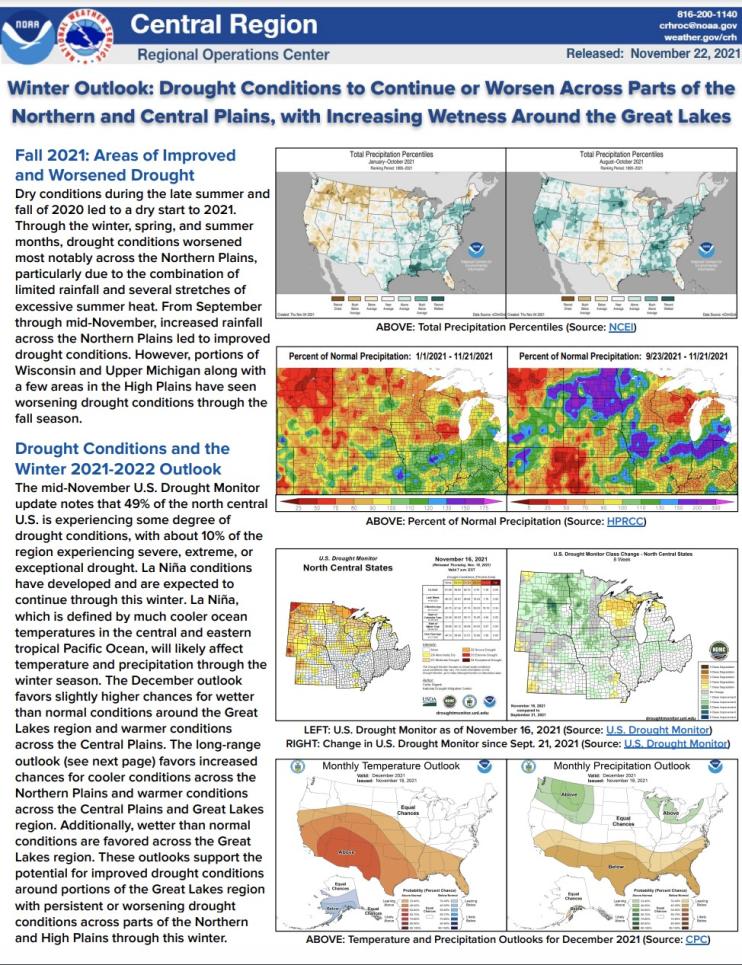
The National Weather Service Central Region developed 2021–2022 Winter Hazard Outlooks in coordination with NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information and National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS); U.S. Department of Agriculture; High Plains Regional Climate Center; and National Interagency Fire Center's Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various Winter hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the North Central U.S.
The Midwest region regularly experiences precipitation extremes, both flood and drought. However, these extremes and their corresponding impacts are typically studied and communicated independently, without consideration of the compound impacts due to a rapid transition from one extreme to the other.
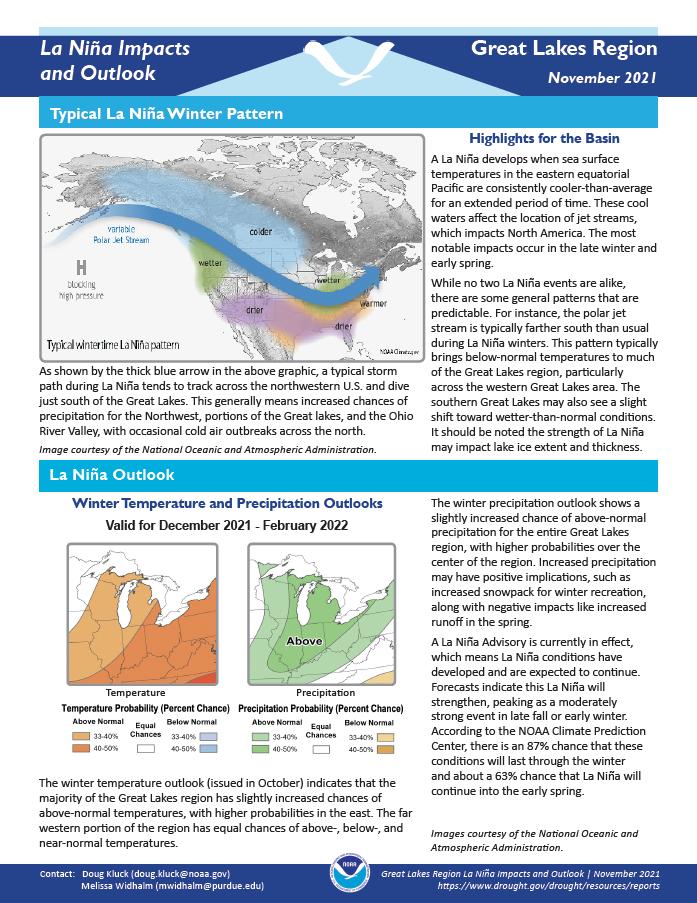
This handout provides information on the typical La Niña winter pattern; the La Niña outlook; potential winter and spring impacts; and comparisons of conditions during previous La Niña years for the Great Lakes region. Updated November 2021.
NOAA’s Regional Climate Services Program created these Outlooks to inform the public about climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the Drought Portal.