For the latest forecasts and critical weather information, visit weather.gov.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Missouri River Basin for December 2021–February 2022. Dated March 2022.
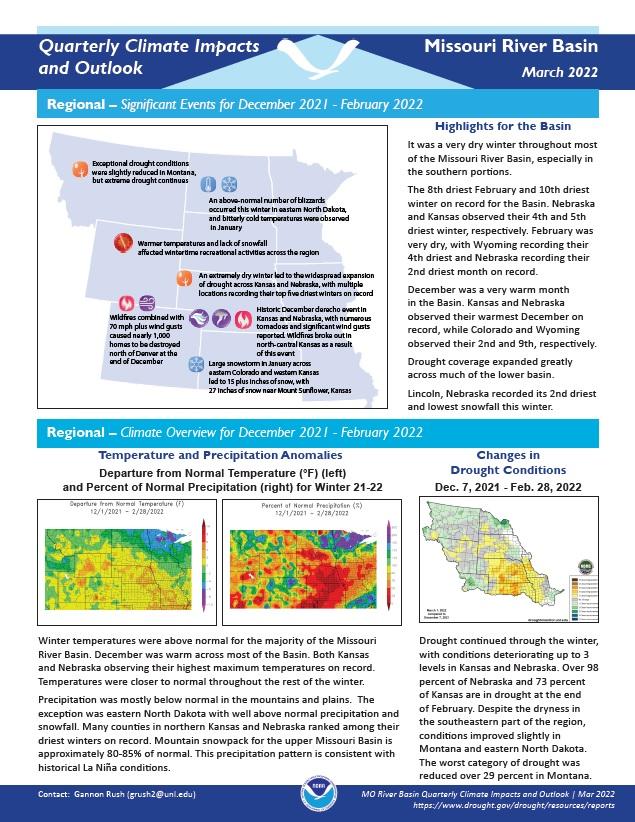
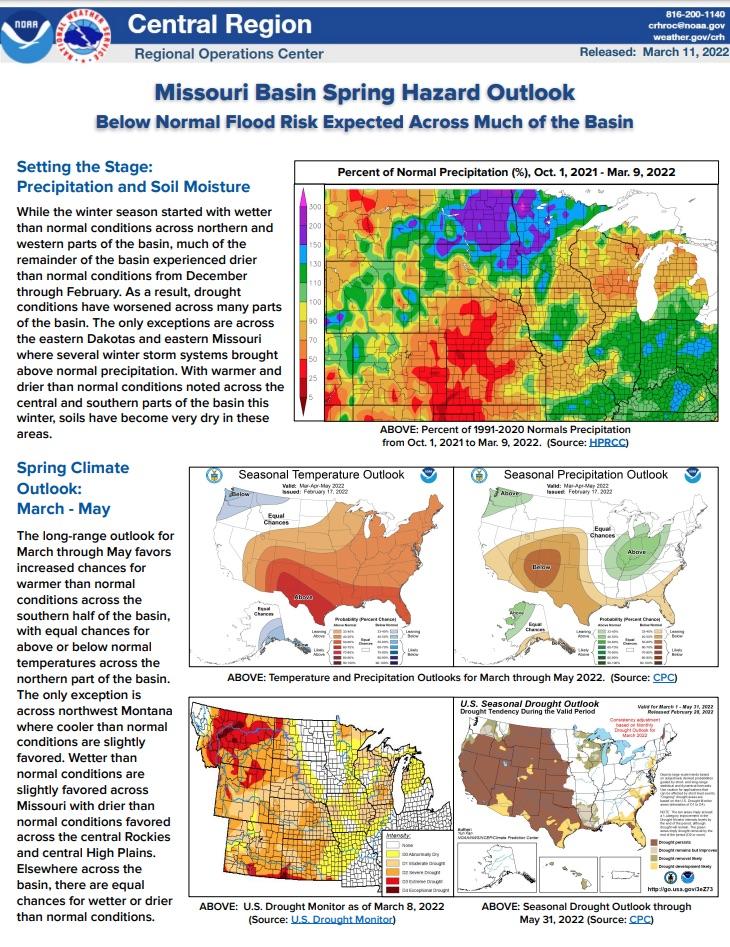
Winter temperatures were above normal for the majority of the Missouri River Basin. Precipitation was mostly below normal in the mountains and plains. The exception was eastern North Dakota with well-above-normal precipitation and snowfall. Many counties in northern Kansas and Nebraska ranked among their driest winters on record.
The National Weather Service developed 2022 Spring Hazard Outlooks in coordination with NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) and National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS); High Plains Regional Climate Center; Midwestern Regional Climate Center; U.S. Department of Agriculture; and National Interagency Fire Centers' Geographic Area Coordination Centers. This outlook highlights the various spring hazards that could occur and potential impacts across the Missouri River Basin.
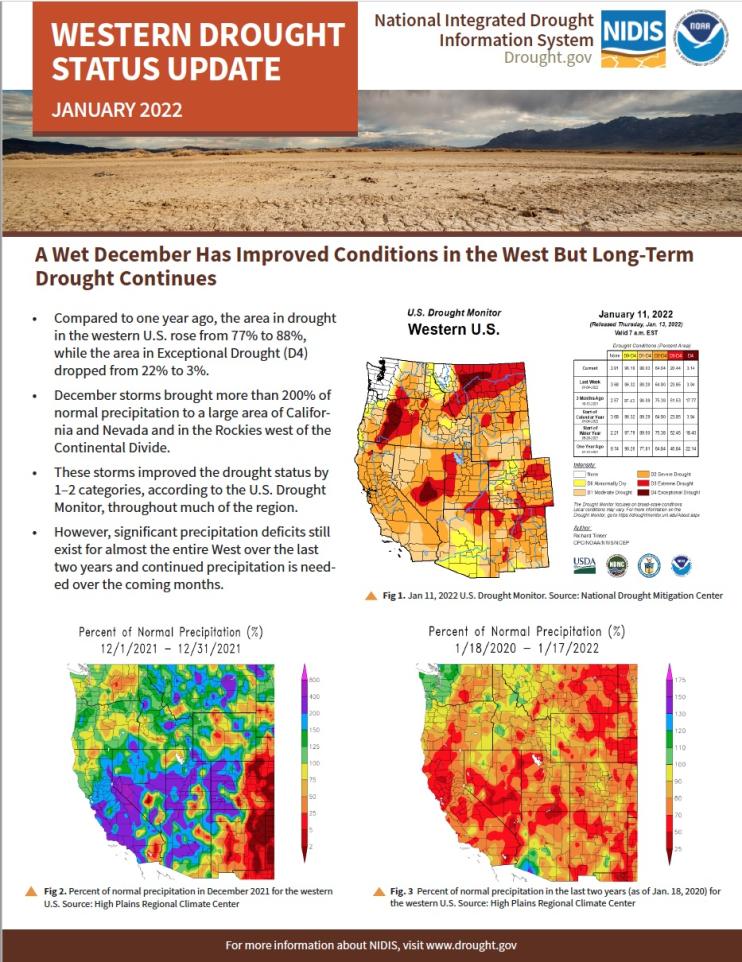
Compared to one year ago, the area in drought in the western U.S. rose from 77% to 88%, while the area in Exceptional Drought (D4) dropped from 22% to 3%. December 2021 storms brought more than 200% of normal precipitation to a large area of California and Nevada and in the Rockies west of the Continental Divide. These storms improved the drought status by 1–2 categories, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor, throughout much of the region.
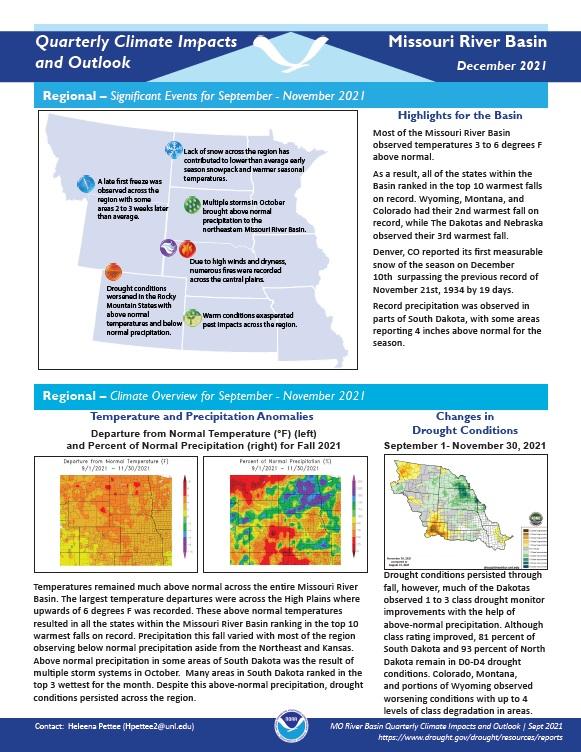
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Missouri River Basin September - November 2021. Dated December 2021.
Temperatures remained much above normal across the entire Missouri River Basin. These above normal temperatures resulted in all the states within the Missouri River Basin ranking in the top 10 warmest falls on record. Precipitation this fall varied with most of the region observing below normal precipitation aside from the Northeast and Kansas.