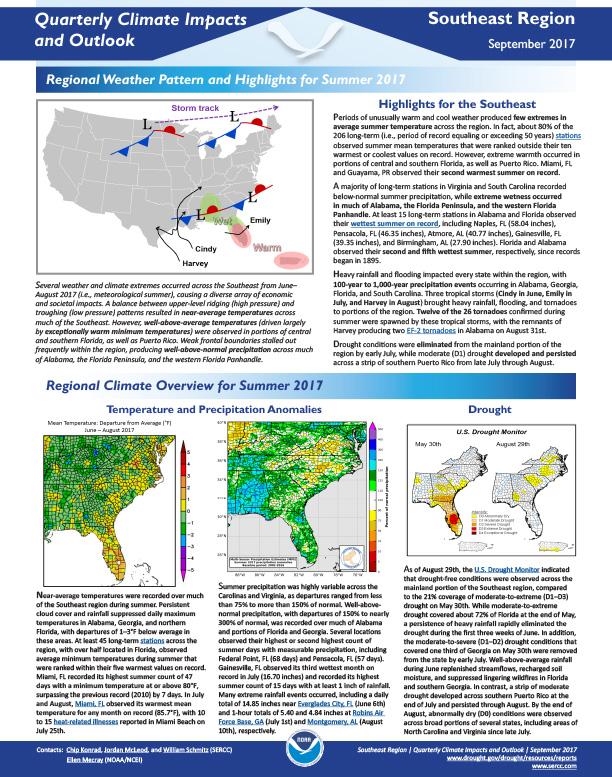
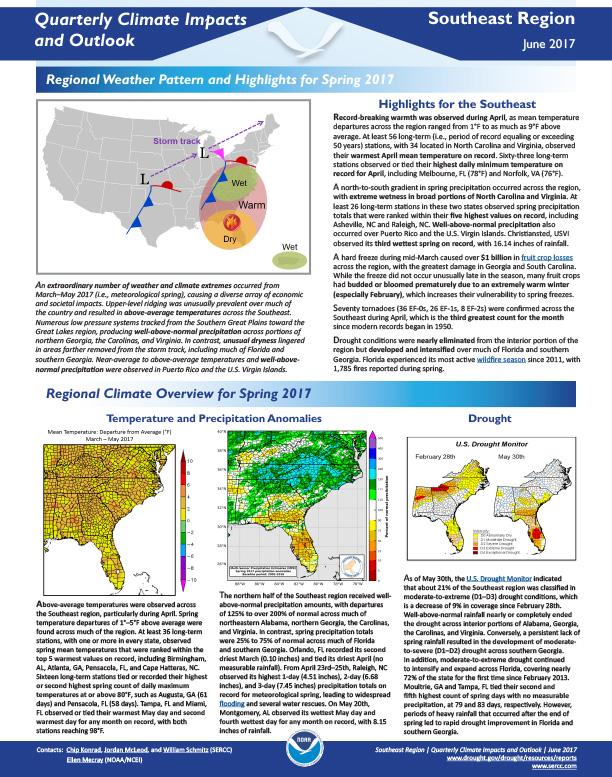
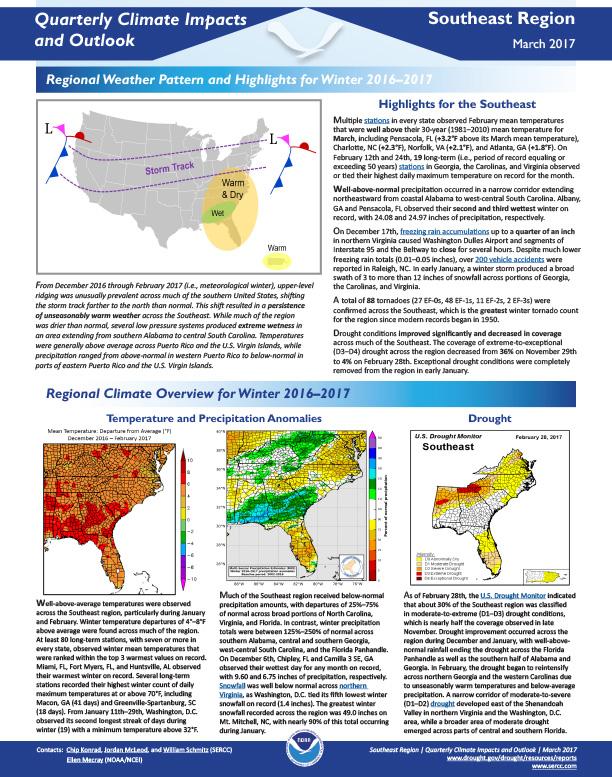
Alabama


Stay Informed: Local Drought Updates
Drought Alert Emails
Get email updates when U.S. Drought Monitor conditions change for your location or a new drought outlook is released.
Southeast DEWS Drought Email List
Get regional drought status updates right to your inbox, as well as drought news, webinars, and other events for the Southeast.
Southeast Climate Monthly Webinars
This webinar series provides the Southeast region with timely information on current and developing climate conditions, such as drought, floods, and tropical storms, as well as climatic events like El Niño and La Niña.
Drought in your area? Tell us how drought is impacting your community by submitting a condition monitoring report. Your submissions help us better understand how drought is affecting local conditions.
State & Regional Resources
Alabama Office of Water Resources | Drought Planning and Management in Alabama
Alabama Drought Management Plan (2024)
Alabama Office of the State Climatologist
Alabama GIS Drought Data Portal
Alabama Department of Economic and Community Affairs | Drought Planning and Management
Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint (ACF) River Basin Drought & Water Dashboard
Alabama-Coosa-Tallapoosa (ACT) River Basin Drought & Water Dashboard
Report: Drought Planning in the Southeast United States
National Weather Service:
- Birmingham Weather Forecast Office
- Huntsville Weather Forecast Office
- Mobile/Pensacola Weather Forecast Office
- Tallahassee Weather Forecast Office
- Southern Region Headquarters
- Southeast River Forecast Center
- Lower Mississippi River Forecast Center
U.S. Drought Monitor
D0 - Abnormally Dry
Abnormally Dry (D0) indicates a region that is going into or coming out of drought, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
D1 – Moderate Drought
Moderate Drought (D1) is the first of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
D2 – Severe Drought
Severe Drought (D2) is the second of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
D3 – Extreme Drought
Extreme Drought (D3) is the third of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
D4 – Exceptional Drought
Exceptional Drought (D4) is the most intense drought category, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
The U.S. Drought Monitor (2000–present) depicts the location and intensity of drought across the country. Every Thursday, authors from NOAA, USDA, and the National Drought Mitigation Center produce a new map based on their assessments of the best available data and input from local observers. The map uses five categories: Abnormally Dry (D0), showing areas that may be going into or are coming out of drought, and four levels of drought (D1–D4). Learn more.
Dry Conditions
D4 (SPI of -2.0 or less)
The 9-month Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is -2.0 or less, indicating exceptional drought (D4) conditions.
D3 (SPI of -1.9 to -1.6)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between -1.9 to -1.6, indicating extreme drought (D3) conditions.
D2 (SPI of -1.5 to -1.3)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between -1.5 to -1.3, indicating severe drought (D2) conditions.
D1 (SPI of -1.2 to -0.8)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between -1.2 to -0.8, indicating moderate drought (D1) conditions.
D0 (SPI of -0.7 to -0.5)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between -0.7 to -0.5, indicating abnormally dry (D0) conditions.
Wet Conditions
W0 (SPI of 0.5 to 0.7)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between 0.5 to 0.7, indicating abnormally wet (W0) conditions.
W1 (SPI of 0.8 to 1.2)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between 0.8 to 1.2, indicating moderate wet (W1) conditions.
W2 (SPI of 1.3 to 1.5)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between 1.3 to 1.5, indicating severe wet (W2) conditions.
W3 (SPI of 1.6 to 1.9)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is between 1.6 to 1.9, indicating extreme wet (W3) conditions.
W4 (SPI of 2.0 or more)
The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) value for this location is 2.0 or greater, indicating exceptional wet (W4) conditions.
Drought results from an imbalance between water supply and water demand. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) measures water supply, specifically precipitation. SPI captures how observed precipitation (rain, hail, snow) deviates from the climatological average over a given time period—in this case, over the 9 months leading up to the selected date. Red hues indicate drier conditions, while blue hues indicate wetter conditions. Data are available monthly from 1895–present.
Dry Conditions
D4 (PMDI of -5.0 or less)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is -5.0 or less, indicating exceptional drought (D4) conditions.
D3 (PMDI of -4.9 to -4.0)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is -4.9 to -4.0, indicating extreme drought (D3) conditions.
D2 (PMDI of -3.9 to -3.0)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is -3.9 to -3.0, indicating severe drought (D2) conditions.
D1 (PMDI of -2.9 to -2.0)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is -2.9 to -2.0, indicating moderate drought (D1) conditions.
D0 (PMDI of -1.9 to -1.0)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is -1.9 to -1.0, indicating abnormally dry (D0) conditions.
Wet Conditions
W0 (PMDI of 1.0 to 1.9)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is 1.0 to 1.9, indicating abnormally wet (W0) conditions.
W1 (PMDI of 2.0 to 2.9)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is 2.0 to 2.9, indicating moderate wet (W1) conditions.
W2 (PMDI of 3.0 to 3.9)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is 3.0 to 3.9, indicating severe wet (W2) conditions.
W3 (PMDI of 4.0 to 4.9)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is 4.0 to 4.9, indicating extreme wet (W3) conditions.
W4 (PMDI of 5.0 or greater)
Tree rings were used to reconstruct a Palmer Modified Drought Index (PMDI) value for each June–August, estimating relative dryness. The PMDI value for this location is 5.0 or greater, indicating exceptional wet (W4) conditions.
In paleoclimatology, proxy climate data (e.g., tree rings, ocean sediments) can allow us to reconstruct past climate conditions before we had widespread instrumental records. The Living Blended Drought Atlas, shown here, estimates average drought conditions each summer (June–August) as far back as the year 0 by combining tree-ring reconstructions and instrumental records. Red hues indicate drier conditions, while blue hues indicate wetter conditions.
Alabama residents in areas of drought, according to the Drought Monitor
driest August on record (since 1895)
wettest January—August on record (since 1895)
Alabama Current Conditions
A number of physical indicators are important for monitoring drought, such as precipitation & temperature, water supply (e.g., streamflow, reservoirs), and soil moisture. Learn more about monitoring drought.
Alabama Precipitation Conditions
Inches of Precipitation
This location received less than 0.01 inch of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 0.01–0.5 inch of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 0.5–1 inch of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 1–2 inches of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 2–4 inches of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 4–6 inches of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received 6–8 inches of precipitation during this 7-day period.
This location received more than 8 inches of precipitation during this 7-day period.
Precipitation Shown as a Percentage of Normal Conditions
<25% of Normal
Precipitation was only 0% to 25% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
25%–50% of Normal
Precipitation was 25% to 50% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
50%–75% of Normal
Precipitation was 50% to 75% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
75%–100% of Normal
Precipitation was 75% to 100% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
100%–150% of Normal
Precipitation was 100% to 150% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
150%–200% of Normal
Precipitation was 150% to 200% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
200%–300% of Normal
Precipitation was 200% to 300% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
>300% of Normal
Precipitation was greater than 300% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
Precipitation Shown as a Percentage of Normal Conditions
<25% of Normal
Precipitation was only 0% to 25% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
25%–50% of Normal
Precipitation was 25% to 50% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
50%–75% of Normal
Precipitation was 50% to 75% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
75%–100% of Normal
Precipitation was 75% to 100% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
100%–150% of Normal
Precipitation was 100% to 150% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
150%–200% of Normal
Precipitation was 150% to 200% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
200%–300% of Normal
Precipitation was 200% to 300% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
>300% of Normal
Precipitation was greater than 300% of the historical average for this location, compared to the same date range from 1991–2020.
This map shows total precipitation (in inches) for the past 7 days. Dark blue shades indicate the highest precipitation amounts.
This map shows precipitation for the past 30 days as a percentage of the historical average (1991–2020) for the same time period. Green/blue shades indicate above-normal precipitation, while brown shades indicate below-normal precipitation.
This map shows precipitation for the past 60 days as a percentage of the historical average (1991–2020) for the same time period. Green/blue shades indicate above-normal precipitation, while brown shades indicate below-normal precipitation.
Precipitation data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Precipitation data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Precipitation data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Drought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAlabama Temperature Conditions
Maximum Temperature (°F)
<0°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is below 0°F.
0–10°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 0–10°F.
10–20°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 10–20°F.
20–30°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 20–30°F.
30–40°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 30–40°F.
40–60°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 40–60°F.
60–70°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 60–70°F.
70–80°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 70–80°F.
80–90°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 80–90°F.
90–100°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between 90–100°F.
>100°F
The 7-day average daily maximum temperature is between greater than 100°F.
Departure from Normal Max Temperature (°F)
>8°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was more than 8°F colder than normal for this location.
6–8°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 6–8°F colder than normal for this location.
4–6°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 4–6°F colder than normal for this location.
3–4°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 3–4°F colder than normal for this location.
1–3°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 1–3°F colder than normal for this location.
0–1°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 0–1°F colder than normal for this location.
0–1°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 0–1°F warmer than normal for this location.
1–3°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 1–3°F warmer than normal for this location.
3–4°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 3–4°F warmer than normal for this location.
4–6°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 4–6°F warmer than normal for this location.
6–8°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 6–8°F warmer than normal for this location.
>8°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was more than 8°F warmer than normal for this location.
Departure from Normal Max Temperature (°F)
>8°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was more than 8°F colder than normal for this location.
6–8°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 6–8°F colder than normal for this location.
4–6°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 4–6°F colder than normal for this location.
3–4°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 3–4°F colder than normal for this location.
1–3°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 1–3°F colder than normal for this location.
0–1°F Below Normal
The average maximum temperature was 0–1°F colder than normal for this location.
0–1°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 0–1°F warmer than normal for this location.
1–3°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 1–3°F warmer than normal for this location.
3–4°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 3–4°F warmer than normal for this location.
4–6°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 4–6°F warmer than normal for this location.
6–8°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was 6–8°F warmer than normal for this location.
>8°F Above Normal
The average maximum temperature was more than 8°F warmer than normal for this location.
This map shows the average maximum daily temperature (°F) for the last 7 days. Blue hues indicate cooler temperatures, while red hues indicate warmer temperatures.
This map shows the average maximum daily temperature for the past 7 days compared to the historical average (1991–2020) for the same 7 days. Negative values (blue hues) indicate colder than normal temperatures, and positive values (red hues) indicate warmer than normal temperatures.
This map shows the average maximum daily temperature for the past 30 days compared to the historical average (1991–2020) for the same 30 days. Negative values (blue hues) indicate colder than normal temperatures, and positive values (red hues) indicate warmer than normal temperatures.
Temperature data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Temperature data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Temperature data are updated daily, with a delay of 3 to 4 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
Air temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAlabama Streamflow Conditions
Streamflow Conditions
Record Low
Estimated streamflow is the lowest value recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Below Normal (<10th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 0–10th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Below Normal (10th–25th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 10th–25th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Normal (25th–75th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 25th–75th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Above Normal (75th–90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 75th–90th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Above Normal (>90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 90th–100th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Record High
Estimated streamflow is the highest value ever measured at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Not Ranked
A flow category has not been computed for this gauge, for example due to insufficient historical data or no current streamflow estimates.
Streamflow Conditions
Record Low
Estimated streamflow is the lowest value recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Below Normal (<10th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 0–10th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Below Normal (10th–25th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 10th–25th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Normal (25th–75th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 25th–75th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Above Normal (75th–90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 75th–90th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Above Normal (>90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 90th–100th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Record High
Estimated streamflow is the highest value ever measured at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Not Ranked
A flow category has not been computed for this gauge, for example due to insufficient historical data or no current streamflow estimates.
Streamflow Conditions
Record Low
Estimated streamflow is the lowest value recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Below Normal (<10th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 0–10th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Below Normal (10th–25th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 10th–25th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Normal (25th–75th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 25th–75th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Above Normal (75th–90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 75th–90th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Much Above Normal (>90th Percentile)
Estimated streamflow is in the 90th–100th percentile of historical streamflow values recorded at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Record High
Estimated streamflow is the highest value ever measured at this gauge on this day of the year. Learn more.
Not Ranked
A flow category has not been computed for this gauge, for example due to insufficient historical data or no current streamflow estimates.
This map shows current streamflow conditions compared to historical conditions for the same day of the year. Click on a streamgage to view current data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
This map shows streamflow conditions averaged over the last 7 days, compared to historical conditions for the same time period. Click on a streamgage to view current data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
This map shows streamflow conditions averaged over the last 28 days, compared to historical conditions for the same time period. Click on a streamgage to view current data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
Periods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can alter the ecological balance of natural systems and harm fish, wildlife, and plant species, as well as the benefits that these ecosystems provide to human communities. The environmental consequences of drought include losses in plant growth; increases in fire and insect outbreaks; altered rates of carbon, nutrient, and water cycling; and local species extinctions.
Learn MoreBecause energy and water are so interdependent, the availability and predictability of water resources can directly affect energy systems. Energy professionals need information on current drought conditions and outlooks in order to make informed decisions on cooling, alternative water supplies, pricing, and infrastructure security.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions that result in low water levels on rivers and other waterways, port and maritime navigation and transportation operations may be limited due to a reduction in available routes and cargo-carrying capacity, resulting in increased costs. In addition, higher temperatures that often coexist with drought can impact roads, airport runways, and rail lines.
Learn MoreAlabama Soil Moisture Conditions
0–100 cm Soil Moisture Percentile
0–2nd Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth is in the bottom 2% (0–2nd percentile) of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
2nd–5th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 2nd to 5th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
5th–10th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 5th to 10th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
10th–20th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 10th to 20th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
20th–30th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 20th to 30th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
30th–70th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 30th to 70th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
70th–80th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 70th to 80th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
80th–90th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 80th to 90th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
90th–95th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 90th to 95th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
95th–98th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth falls between the 95th to 98th percentile of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
98th–100th Percentile
Soil moisture at 0–100cm depth is in the top 2% (98th to 100th percentile) of historical measurements for this day of the year. Learn more.
Soil Moisture Anomaly
An accurate depiction of soil moisture conditions can provide valuable insights for agricultural monitoring, weather prediction, and drought and flood early warning.
This map shows the moisture content of the top 1 meter of soil compared to historical conditions from 1981–2013, based on NASA's Short-term Prediction and Transition Center – Land Information System (SPoRT-LIS).
Red and orange hues indicate drier soils, while greens and blues indicate greater soil moisture.
An accurate depiction of soil moisture conditions can provide valuable insights for agricultural monitoring, weather prediction, and drought and flood early warning.
This map shows the moisture content of the top 1 meter of soil, according to NASA's Crop Condition and Soil Moisture Analytics tool (Crop-CASMA). It relies on remotely sensed soil moisture data derived from NASA missions.
Soil moisture is shown as a deviation from average soil moisture conditions from 2015–present. Brown hues indicate below-average soil moisture, and blue hues indicate above-average soil moisture.
This map updates daily with data from NASA's Short-term Prediction and Transition Center – Land Information System (SPoRT-LIS).
Data are updated daily, with a 3-day delay.
Soil moisture plays an important role in drought and flood forecasting, agricultural monitoring, forest fire prediction, water supply management, and other natural resource activities. Soil moisture observations can forewarn of impending drought or flood conditions before other more standard indicators are triggered.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought can result in reduced growth rates, increased stress on vegetation, and alterations or transformations to the plant community and/or the entire ecosystem. During periods of drought, plants increase their demand for water through increased evapotranspiration and longer growing seasons.
Learn MoreSoil moisture plays an important role in drought and flood forecasting, agricultural monitoring, forest fire prediction, water supply management, and other natural resource activities. Soil moisture observations can forewarn of impending drought or flood conditions before other more standard indicators are triggered.
Learn MoreOutlooks & Forecasts for Alabama
Predicting drought in Alabama depends on the ability to forecast precipitation and temperature within the context of complex climate interactions. View more outlooks & forecasts.
Future Precipitation & Temperature Conditions
Predicted Inches of Precipitation
Less than 0.01 inch
0.01 to 0.1 inch
0.1 to 0.25 inch
0.25 to 0.5 inch
0.5 to 0.75 inch
0.75 to 1 inch
1 to 1.25 inches
1.25 to 1.5 inches
1.5 to 1.75 inches
1.75 to 2 inches
1.5 to 2 inches
2 to 2.5 inches
2.5 to 3 inches
3 to 4 inches
4 to 5 inches
5 to 7 inches
7 to 10 inches
10 to 15 inches
15 to 20 inches
More than 20 inches
Probability of Below-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Precipitation
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal precipitation during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal precipitation during this period.
Probability of Below-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Below Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Below Normal
There is a >90% chance of below-normal temperatures during this period.
Probability of Above-Normal Temperatures
33%–40% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 33%–40% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
40%–50% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 40%–50% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
50%–60% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 50%–60% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
60%–70% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 60%–70% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
70%–80% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 70%–80% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
80%–90% Chance of Above Normal
There is an 80%–90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
>90% Chance of Above Normal
There is a >90% chance of above-normal temperatures during this period.
Near-Normal
Odds favor near-normal temperatures during this period.
This map shows the amount of liquid precipitation (in inches) expected to fall over the next 7 days, according to the National Weather Service.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal precipitation 8 to 14 days in the future.
This map shows the probability (percent chance) of above-normal, near-normal, or below-normal temperature 8 to 14 days in the future.
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast maps on Drought.gov are updated once a day and are valid from 7 a.m. Eastern that day.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 8–14 day outlooks daily.
The Climate Prediction Center updates their 8–14 day outlooks daily.
Drought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought Outlooks for Alabama
Drought Is Predicted To...
Drought Persists
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought conditions will persist.
Drought Improves
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that existing drought conditions will improve (but not be removed).
Drought Is Removed
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will be removed.
Drought Develops
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will develop.
No Drought Present
According to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center, there is no drought, and is drought development is not predicted.
Drought Is Predicted To...
Drought Persists
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought conditions will persist.
Drought Improves
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that existing drought conditions will improve (but not be removed).
Drought Is Removed
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will be removed.
Drought Develops
During this time period, NOAA's Climate Prediction Center predicts that drought will develop.
No Drought Present
According to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center, there is no drought, and is drought development is not predicted.
2-4 Week Hazard Outlook
Risk of Rapid Onset Drought
National Weather Service forecasters predict that rapid drought development (also known as "flash drought") may occur in the coming 2–4 weeks.
The Monthly Drought Outlook predicts whether drought will develop, remain, improve, or be removed in the next calendar month.
The Seasonal Drought Outlook predicts whether drought will develop, remain, improve, or be removed in the next 3 months or so.
This National Weather Service hazard outlook map shows the risk of rapid onset drought (flash drought) development during the next 2–4 weeks.
Forecasters use initial conditions, like existing dryness (e.g., soil moisture), temperature, and precipitation outlooks, to assess the risk of rapid drought development. Rapid onset drought risk areas (yellow) can give users, such as farmers making decisions about planting and supplemental irrigation, an early warning of the potential for hot and dry conditions.
The Climate Prediction Center issues its Monthly Drought Outlooks on the last day of the calendar month.
The Climate Prediction Center issues its Seasonal Drought Outlooks on the third Thursday of each calendar month. Sometimes, the map is adjusted on the last day of the month to maintain consistency with the Monthly Drought Outlook.
National Weather Service (NWS) forecasters issue rapid onset drought (ROD) risk areas on Thursdays, with the potential for updates on the following Mondays, from April 1–October 31.
The NWS Climate Prediction Center hazards outlook is issued between 2–5 p.m. ET, and this Drought.gov map updates at 7 p.m. ET.
Snow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreSnow drought is a period of abnormally low snowpack for the time of year. Snowpack typically acts as a natural reservoir, providing water throughout the drier summer months. Lack of snowpack storage, or a shift in timing of snowmelt, can be a challenge for drought planning.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreDuring drought conditions, fuels for wildfire, such as grasses and trees, can dry out and become more flammable. Drought can also increase the probability of ignition and the rate at which fire spreads. Temperature, soil moisture, humidity, wind speed, and fuel availability (vegetation) are all factors that interact to influence the frequency of large wildfires.
Learn MoreAir temperature can have wide-ranging effects on natural processes. Warmer air temperatures increase evapotranspiration—which is the combination of evaporation from the soil and bodies of water and transpiration from plants—and lower soil moisture.
Learn MoreFlash drought is the rapid onset or intensification of drought. Unlike slow-evolving drought, which is caused by a decline in precipitation, flash drought occurs when low precipitation is accompanied by abnormally high temperatures, high winds, and/or changes in radiation. These sometimes-rapid changes can quickly raise evapotranspiration rates and remove available water from the landscape.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreExtreme weather events can interact or cascade—where one disaster event triggers or changes the probability of another event. For example, drought conditions can increase the probability of large-scale wildfires, and droughts are often accompanied by extreme heat. By including drought in multi-hazard planning, a community can consolidate its resources and develop coordinated responses before a disaster.
Learn MoreThe U.S. Drought Monitor depicts the location and intensity of drought across the country. The map uses 5 classifications: Abnormally Dry (D0), showing areas that may be going into or are coming out of drought, and four levels of drought (D1–D4). The map is jointly produced by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and National Drought Mitigation Center. Authors from these agencies rotate creating the map each week, using both physical indicators and input from local observers.
This map is used by the U.S. Department of Agriculture to trigger some disaster declarations and loan eligibility. Individual states and water supply planning may use additional information to inform their declarations and actions. Learn more.
How has drought impacted this state in the past? Explore historical Drought Monitor maps.
The U.S. Drought Monitor 1-week change map shows where drought has improved, remained the same, or worsened since the previous week's Drought Monitor.
The U.S. Drought Monitor depicts the location and intensity of drought across the country, using 5 classifications (D0–D4). Green hues indicate conditions improved, while yellow/orange hues indicate degradations.
The Short-Term Multi-Indicator Drought Index (MIDI) estimates current short-term drought conditions across the U.S. by combining several indicators of drought into a single, computer-generated map.
Specifically, this map approximates drought conditions from changes in precipitation and moisture over the past 3 months. Short-term moisture deficits can impact non-irrigated agriculture, topsoil moisture, range and pasture conditions, and more. Long-term droughts (lasting months to years) can have different impacts.
This experimental map is based on methodology from the NOAA National Weather Service’s Climate Prediction Center. Learn how this map is made.
The Long-Term Multi-Indicator Drought Index (MIDI) estimates current long-term drought conditions across the U.S. by combining several indicators of drought into a single, computer-generated map.
Specifically, this map approximates drought conditions from longer-term changes in precipitation and moisture going back up to 5 years. Long-term drought conditions (lasting months to years) can impact irrigated agriculture, groundwater, and reservoir levels, and can increase wildfire intensity and severity.
This experimental map is based on methodology from the NOAA National Weather Service’s Climate Prediction Center. Learn how this map is made.
A drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought & Dryness Categories
% of ALAbnormally Dry
Abnormally Dry (D0) indicates a region that is going into or coming out of drought. View typical impacts by state.
Moderate Drought
Moderate Drought (D1) is the first of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
Severe Drought
Severe Drought (D2) is the second of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
Extreme Drought
Extreme Drought (D3) is the third of four drought categories (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
Exceptional Drought
Exceptional Drought (D4) is the most intense drought category, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. View typical impacts by state.
Total Area in Drought (D1–D4)
Percent area of Alabama that is currently in drought (D1–D4), according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
Drought Change Since Last Week
3-Category Degradation
Drought/dryness has worsened by 3 categories, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
2-Category Degradation
Drought/dryness has worsened by 2 categories, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
1-Category Degradation
Drought/dryness has worsened by 1 category, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
No Change
There has been no change in drought conditions at this location.
1-Category Improvement
Drought/dryness has improved by 1 category, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
2-Category Improvement
Drought/dryness has improved by 2 categories, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
3-Category Improvement
Drought/dryness has improved by 3 categories, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor.
Dry Conditions
D4: Exceptional Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 98% to 100% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D3: Extreme Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 95% to 98% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D2: Severe Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 90% to 95% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D1: Moderate Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 80% to 90% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D0: Abnormally Dry
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 70% to 80% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
Wet Conditions
W0: Abnormally Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 70% to 80% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W1: Moderate Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 80% to 90% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W2: Severe Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 90% to 95% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W3: Extreme Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 95% to 98% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W4: Exceptional Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 98% to 100% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
Dry Conditions
D4: Exceptional Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 98% to 100% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D3: Extreme Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 95% to 98% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D2: Severe Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 90% to 95% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D1: Moderate Drought
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 80% to 90% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
D0: Abnormally Dry
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are drier than 70% to 80% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
Wet Conditions
W0: Abnormally Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 70% to 80% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W1: Moderate Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 80% to 90% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W2: Severe Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 90% to 95% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W3: Extreme Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 95% to 98% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
W4: Exceptional Wet
This map integrates multiple drought indices measuring precipitation and moisture into one computer-generated drought map, with a reference period of 1979–present. According to these indices, current conditions are wetter than 98% to 100% of past conditions. Learn more about these categories.
The U.S. Drought Monitor depicts the location and intensity of drought across the country. The map uses 5 classifications: Abnormally Dry (D0), showing areas that may be going into or are coming out of drought, and four levels of drought (D1–D4). The map is jointly produced by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and National Drought Mitigation Center. Authors from these agencies rotate creating the map each week, using both physical indicators and input from local observers.
This map is used by the U.S. Department of Agriculture to trigger some disaster declarations and loan eligibility. Individual states and water supply planning may use additional information to inform their declarations and actions. Learn more.
How has drought impacted this state in the past? Explore historical Drought Monitor maps.
The U.S. Drought Monitor 1-week change map shows where drought has improved, remained the same, or worsened since the previous week's Drought Monitor.
The U.S. Drought Monitor depicts the location and intensity of drought across the country, using 5 classifications (D0–D4). Green hues indicate conditions improved, while yellow/orange hues indicate degradations.
The Short-Term Multi-Indicator Drought Index (MIDI) estimates current short-term drought conditions across the U.S. by combining several indicators of drought into a single, computer-generated map.
Specifically, this map approximates drought conditions from changes in precipitation and moisture over the past 3 months. Short-term moisture deficits can impact non-irrigated agriculture, topsoil moisture, range and pasture conditions, and more. Long-term droughts (lasting months to years) can have different impacts.
This experimental map is based on methodology from the NOAA National Weather Service’s Climate Prediction Center. Learn how this map is made.
The Long-Term Multi-Indicator Drought Index (MIDI) estimates current long-term drought conditions across the U.S. by combining several indicators of drought into a single, computer-generated map.
Specifically, this map approximates drought conditions from longer-term changes in precipitation and moisture going back up to 5 years. Long-term drought conditions (lasting months to years) can impact irrigated agriculture, groundwater, and reservoir levels, and can increase wildfire intensity and severity.
This experimental map is based on methodology from the NOAA National Weather Service’s Climate Prediction Center. Learn how this map is made.
This map is released every Thursday morning, with data valid through Tuesday at 7am Eastern.
U.S. Drought Monitor change maps are released every Thursday morning, with data valid through Tuesday at 7 am Eastern.
The drought indices used in this map are based on the GridMET dataset and use a reference period of 1979–present. This map is updated every 5 days, with a delay of 4 to 5 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
The drought indices used in this map are based on the GridMET dataset and use a reference period of 1979–present. This map is updated every 5 days, with a delay of 4 to 5 days to allow for data collection and quality control.
A drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreDrought can reduce the water availability and water quality necessary for productive farms, ranches, and grazing lands, resulting in significant negative direct and indirect economic impacts to the agricultural sector. Monitoring agricultural drought typically focuses on examining levels of precipitation, evaporative demand, soil moisture, and surface/groundwater quantity and quality.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
Learn MoreA drought index combines multiple drought indicators (e.g., precipitation, temperature, soil moisture) to depict drought conditions. For some products, like the U.S. Drought Monitor, authors combine their analysis of drought indicators with input from local observers. Other drought indices, like the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), use an objective calculation to describe the severity, location, timing, and/or duration of drought.
Learn MoreDrought is defined as the lack of precipitation over an extended period of time, usually for a season or more, that results in a water shortage. Changes in precipitation can substantially disrupt crops and livestock, influence the frequency and intensity of severe weather events, and affect the quality and quantity of water available for municipal and industrial use.
Learn MorePeriods of drought can lead to inadequate water supply, threatening the health, safety, and welfare of communities. Streamflow, groundwater, reservoir, and snowpack data are key to monitoring and forecasting water supply.
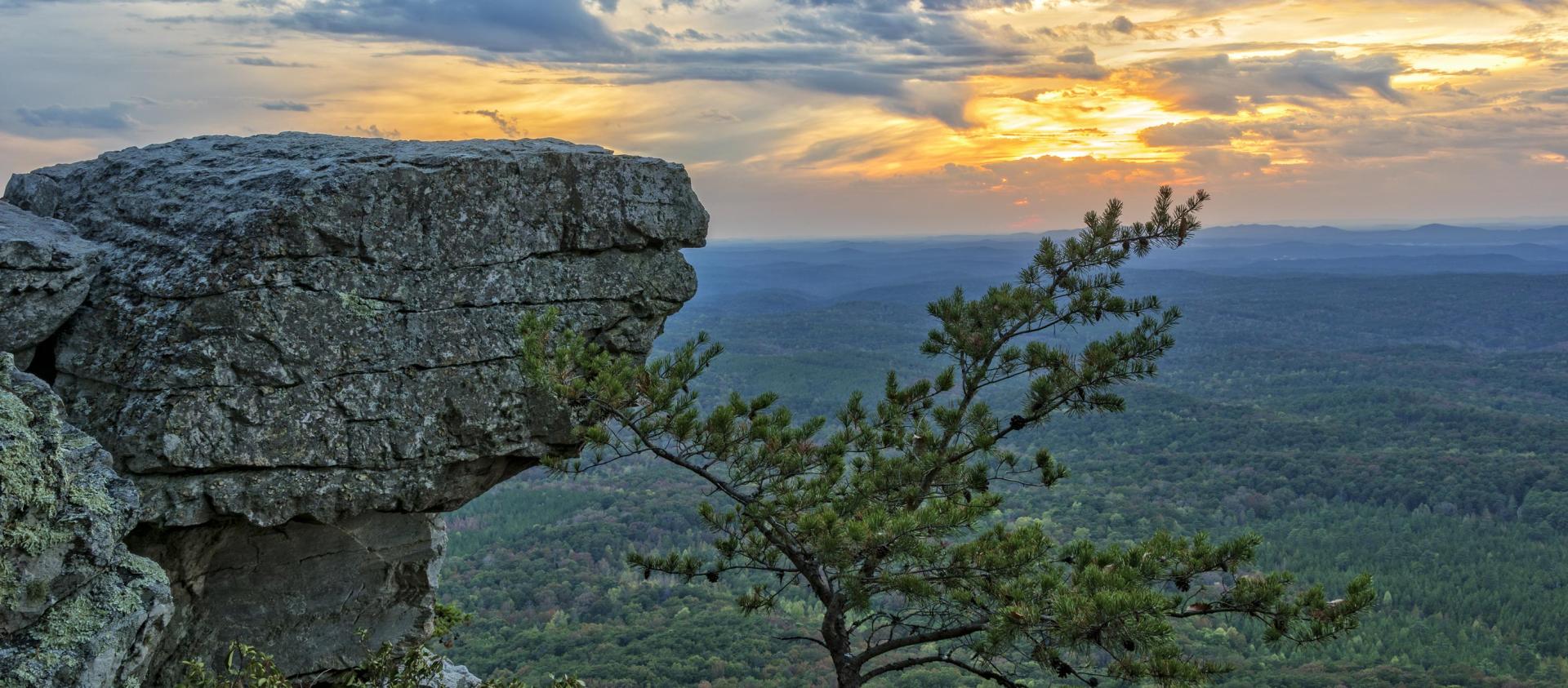
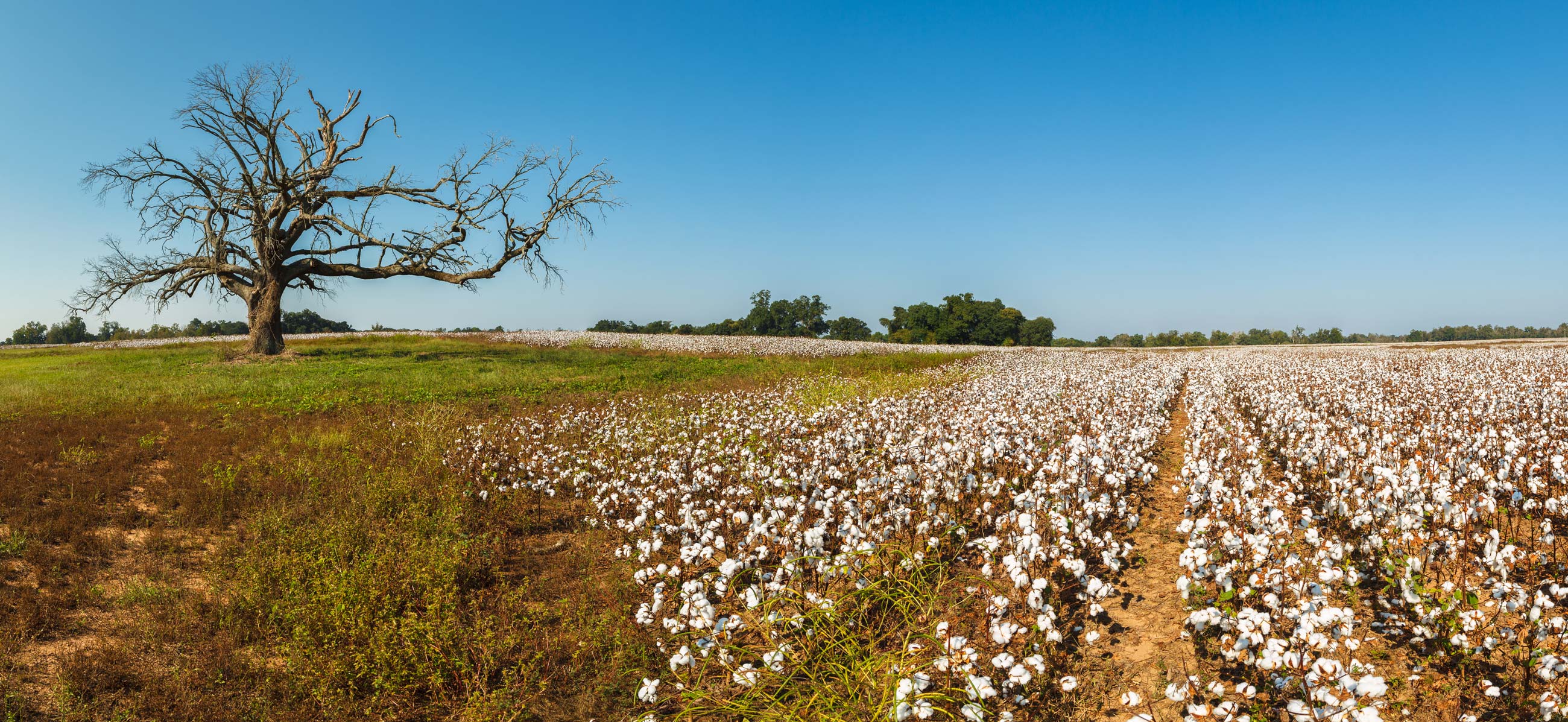
Learn MoreAlabama is no stranger to drought. Recent droughts experienced in 2000, 2007–2008, and 2011–2012 are especially noteworthy, along with the flash droughts in 2016 and the fall of 2019. The Alabama Office of the State Climatologist and the Office of Water Resources (OWR) monitor drought across the state. The climate office uses precipitation, streamflow, soil moisture, and temperature data to provide input to the U.S. Drought Monitor, and the OWR utilizes similar information to inform local watershed management. OWR is assisted by the Alabama Drought Assessment and Planning Team, which gets technical input from their drought Monitoring and Impact Group subcommittee. Through this partnership, OWR releases drought declarations that help local watershed managers make vital water usage decisions.
Droughts in Alabama and across the Southeast can have far-reaching impacts on agriculture, water availability, and wildfires. Drought conditions can also develop rapidly in the Southeast, especially when the lack of rain and high temperatures combine to quickly increase the loss of water from the landscape via evapotranspiration. There is increased regional awareness of how these rapid-onset droughts, sometimes referred to as "flash droughts," can cause significant agricultural economic impacts.
NOAA’s National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) launched the Southeast Drought Early Warning System (DEWS) in 2020, which includes Alabama, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia. The Southeast DEWS is a network of regional and national partners that share information and coordinate actions to help communities in the region cope with drought.
Reach out to Elliot Wickham, the Regional Drought Coordinator for this region, for more information, or sign up for the Southeast DEWS newsletter.
Alabama State Drought Resources
State Drought Websites:
Drought Planning and Management in Alabama
Alabama GIS Drought Data Portal
State Drought Agencies & Committees:
Alabama Department of Economic and Community Affairs, Office of Water Resources
Alabama Drought Assessment and Planning Team
State Drought Plan: Alabama Drought Management Plan (2024)
State Climate Office: Alabama Office of the State Climatologist
Historical Drought Conditions in Alabama
Drought is a normal climate pattern that has occurred in varying degrees of length, severity, and size throughout history. Below, you can look back at past drought conditions for Alabama according to 3 historical drought indices. The U.S. Drought Monitor is a weekly map that shows the location and intensity of drought across the country since 2000. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) is a monthly depiction of drought based on precipitation (with data going back to 1895). And the paleoclimate data uses tree-ring reconstructions to estimate drought conditions before we had widespread instrumental records, going back to the year 0 for some parts of the U.S. View more historical conditions.